Food Waste Management Market Size, Share, Growth Opportunity Analysis Report by Waste Type (Food Production Waste, Food Processing Waste, Distribution & Supply Chain Waste, Retail Waste, Household/ Consumer-Level Waste, Post-consumer Plate Waste and Others), Process, Source, Organization Size, Service Type, Treatment Method, End Use and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, Africa, and South America) – Global Industry Data, Trends, and Forecasts, 2025–2035.
|
|
|
Segmental Data Insights |
|
|
Demand Trends |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Strategic Development |
|
|
Future Outlook & Opportunities |
|
Food Waste Management Market Size, Share, and Growth
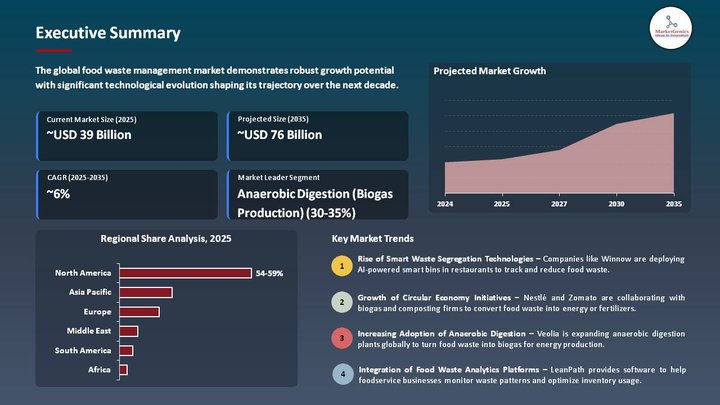
With a significant compounded annual growth rate of 6.1% from 2025-2035, global food waste management market is poised to be valued at USD 75.9 Billion in 2035. The growth drivers behind the worldwide food waste management market are the increased acceptance of composting and anaerobic digestion technologies and an increase in regulatory mandates to reduce waste in the retail and hospitality sectors.
In April 2025, FCC Environment Ltd. launched a large-scale food waste composting facility in the UK capable of processing 50,000 tonnes annually, aimed at serving both municipal contracts and commercial clients. The initiative supports the country’s national food waste separation mandate and promotes circular economy practices through high-quality compost production. Steve Longdon, Managing Director of FCC Environment, highlighted that the project aligns with the company’s strategy to expand sustainable waste recovery infrastructure across the UK and meet increasing demand from local authorities. This strategic expansion strengthens FCC Environment’s leadership in municipal food waste recycling and supports national landfill diversion goals.
The SMARTFOOD WASTE system was installed by BioHiTech Global at a major U.S. supermarket chain in May 2025, converting unsellable produce into bioenergy on-site. The implementation has proven to be tremendously operationally efficient with waste pickups reduced by 50% and additional renewable energy generated. Enhanced technology deployment and stricter regulations further accelerate the market growth making food waste management more efficient and sustainable.
Global food waste management opportunities or avenues include bioenergy production, manufacturing of organic fertilizers, and smart technologies for tracking waste. These sectors place emphasis on valorization of food waste into renewable resources and on digital monitoring tools to help with sustainability goals. This integration with neighboring sectors opens up more value chains, thereby uplifting the value of the market as a whole and driving innovation.

Food Waste Management Market Dynamics and Trends
Driver: Corporate Sustainability & ESG Mandates
- In corporate sustainability goals and ESG mandate, increased emphasis is being placed on investment in food waste management infrastructure. Large retailers, food processors, and hospitality chains all face growing consumer and regulatory pressure to limit their landfill contributions and to report sustainability metrics.
- For instance, in June 2025, Waste Management Inc. rolled out its EcoCycle Commercial Organics platform to 50 supermarkets in California, wherein it provided customized composting services and a full range of waste reporting dashboards for corporate ESG compliance. By integrating on-site composting bins with real-time data analytics, this system has optimized both disposal cost and the transparency of percentage diversion. The more companies start valuing carbon and waste footprints monetarily, the more such turnkey solutions are getting adopted.
- Increased corporate accountability and ESG frameworks accelerate the rollout of scalable and tech-enabled food waste management opportunity across industries.
Restraint: High Capital Expenditure for Advanced Treatment Systems
- Scaling-up remains a somewhat limited opportunity, especially in middle-income countries, due to the relatively high initial investment for advanced systems of food waste treatment, i.e., anaerobic digesters, industrial composters, thermal hydrolysis units. While small-scale setups may promise high returns over time, many of them lack the cash upfront for capital expenses (CapEx) without grants and/or financing.
- In April of 2025, Veolia withdrew from the development of a proposed anaerobic digestion plant in Eastern Europe due to prohibitive costs and the absence of governmental subsidies for the project. The cancellation of the project delayed food-waste-to-energy initiatives at the regional scale and the local organic waste streams remained largely unused. Deployment of large-scale systems will remain at the bare minimum, unless financial models supported by incentives or lease-to-own and pay-as-you-go options are implemented at the mass level.
- Those upfront investment barriers limit not only pilot-scale projects but also widespread deployment of advanced food-waste-treatment technologies.
Opportunity: Integration with Circular Bioeconomy
- Consequently, switching the storyline toward a circular bioeconomy where food waste is reused as feedstock for bio-based chemicals, animal feed, or biomaterials creates lucrative diversification opportunities for food waste management providers.
- In May 2025, Novozymes, a biotechnology company, partnered with OlioTech to pilot the upcycling of low-value brewery spent grains into enzyme-infused animal feed pellets. This proof-of-concept facility utilized in Denmark showed a 20% improvement in animal feed efficiency and diverted thousands of tons of byproducts from being thrown into landfills annually. By applying further enzymatic treatment to fermentation processes, companies can capitalize on higher-value revenue streams originating from waste outputs. This model feeds nutrient cycling, limits reliance on virgin materials, and enriches sustainable agriculture.
- Combining management of food waste and its bio-based valorization opens new commercial avenues and empties deeper circularity into resource use.
Key Trend: Digitalization & AI-Powered Waste Monitoring
- In the case of food-waste management, one can now talk of digital transformation; it has shifted it from reactive disposal to active optimization. So far, specialized smart sensors, computer vision systems, and IoT waste bins get the scale of view of waste volumes, types, and sources.
- LeanPath implemented successfully in July 2025 the AI-powered food-waste tracking system in 200 large hotel kitchens across the USA, with live loss alerts through a simple app. The chefs get notified with itemized alerts such as "40 percent leftover on Monday's sautéed vegetables," initiating behavior modifications and inventory changes. On the other hand, the data portal consolidates waste trends for benchmarking across chains. Predictive analytics then goes about to identify up to 30% waste reduction and tighten procurement and menu decisions.
- Digital transformation evolves management strategies focused on waste reduction with the overall aim of conserving the environment and operational efficiency.
Food Waste Management Market Analysis and Segmental Data
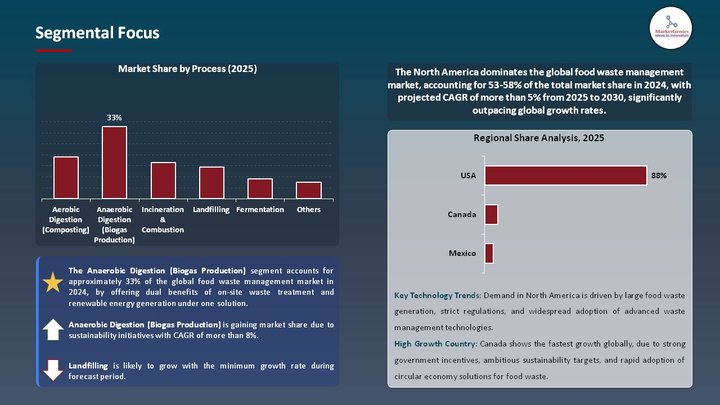
Based on Process, the Anaerobic Digestion (Biogas Production) Segment Retains the Largest Share
- The anaerobic digestion (Biogas Production) segment holds major share ~33% in the global food waste management market. By offering dual benefits of on-site waste treatment and renewable energy generation under one solution. This started in 2025, when Engie North America commissioned its largest-scale commercial food-waste-to-energy AD facility in Pennsylvania, producing 2.5 MW of biogas electricity from 50,000-plus tons of waste yearly consisting of restaurant and supermarket waste. This turnkey solution attracts municipalities and companies seeking integrated environmental and energy solutions, thereby making AD an investment of choice.
- Furthermore, with tightening regulations around methane and carbon, are speeding up AD adoption. Compost may reduce landfill emissions and give revenues from biogas and carbon offset to improve ROI.
- The ability of the AD segment to turn wastes into clean energy and compliance assets is fast driving its share in food waste management.
North America Dominates Global Food Waste Management Market in 2025 and Beyond
- North America experiences the highest demand for food waste management, considering strict governmental regulations, the immense food waste created on a per capita basis, and the existence of highly developed waste treatment infrastructure. In March 2025, the city of New Haven started a comprehensive curbside composting program supported by state infrastructure upgrades to keep residential food waste out of landfills. These include programs to encourage color-coded waste segregation and access to organic bins, both attractive to the public for investment in sustainable waste solutions.
- Concurrently, Washington, D.C managed to divert thousands of pounds of organic waste within weeks by deploying smart waste bins with sensors to monitor volumes of food waste and thus rodent activity. On a much wider regional scale, this illustrates an integration of smart technologies and municipal action plans to comprehensively confront food waste.
- North America's leadership, thereby, is sustained through policies enforcement, funding, and adoption of smart technology.
Food Waste Management Market Ecosystem
Key players in the global food waste management market include prominent companies such as Veolia Environnement S.A., Waste Management, Inc., Suez S.A., Republic Services, Inc., Remondis SE & Co. KG and Other Key Players.
The food waste management sector is moderately consolidated, with Tier 1 players such as Waste Management, Veolia, and Suez leading in terms of activity and service offerings worldwide. Tier 2 and 3 players, such as BioHiTech Global and Harvest Power, focus on niche or regional markets. On the buyer's side, concentration is moderate, with municipalities and large food service contractors as key players. Supplier concentration is moderate generally, with dependence on waste processing technology, logistics, and regulatory compliance as the critical factors on the value-chain side.

Recent Development and Strategic Overview:
- In June 2025, Thiruvananthapuram city tried an experiment at actually compressing biodegradable waste in the high-volume zones before aerobic composting. It improves hygiene, lowers costs in transportation, and channels institutional waste to local pig farms: a circular economy model handling around 65–70 tonnes on a daily basis. This is a new paradigm of municipal-science interface.
- In May 2025, Zest and Nestle injected AI monitoring into a factory, cutting edible food waste by 87% in two weeks. This saved 700 tonnes of surplus-edible food (around 1.5 million meals) and prevented 1,400 tonnes of CO₂ emissions, with plans to upscale through a subscription model across Nestlé's supply chain.
Report Scope
|
Detail |
|
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 39.5 Bn |
|
Market Forecast Value in 2035 |
USD 75.9 Bn |
|
Growth Rate (CAGR) |
6.1% |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 – 2035 |
|
Historical Data Available for |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Market Size Units |
US$ Billion for Value |
|
Report Format |
Electronic (PDF) + Excel |
|
North America |
Europe |
Asia Pacific |
Middle East |
Africa |
South America |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Companies Covered |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Food Waste Management Market Segmentation and Highlights
|
Segment |
Sub-segment |
|
By Waste Type |
|
|
By Process |
|
|
By Source |
|
|
By Organization Size |
|
|
By Deployment Mode |
|
|
By Service Type |
|
|
By Treatment Method |
|
|
By End Use |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Table of Contents
- 1. Research Methodology and Assumptions
- 1.1. Definitions
- 1.2. Research Design and Approach
- 1.3. Data Collection Methods
- 1.4. Base Estimates and Calculations
- 1.5. Forecasting Models
- 1.5.1. Key Forecast Factors & Impact Analysis
- 1.6. Secondary Research
- 1.6.1. Open Sources
- 1.6.2. Paid Databases
- 1.6.3. Associations
- 1.7. Primary Research
- 1.7.1. Primary Sources
- 1.7.2. Primary Interviews with Stakeholders across Ecosystem
- 2. Executive Summary
- 2.1. Global Food Waste Management Market Outlook
- 2.1.1. Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 2.1.2. Compounded Annual Growth Rate Analysis
- 2.1.3. Growth Opportunity Analysis
- 2.1.4. Segmental Share Analysis
- 2.1.5. Geographical Share Analysis
- 2.2. Market Analysis and Facts
- 2.3. Supply-Demand Analysis
- 2.4. Competitive Benchmarking
- 2.5. Go-to- Market Strategy
- 2.5.1. Customer/ End Use Industry Assessment
- 2.5.2. Growth Opportunity Data, 2025-2035
- 2.5.2.1. Regional Data
- 2.5.2.2. Country Data
- 2.5.2.3. Segmental Data
- 2.5.3. Identification of Potential Market Spaces
- 2.5.4. GAP Analysis
- 2.5.5. Potential Attractive Price Points
- 2.5.6. Prevailing Market Risks & Challenges
- 2.5.7. Preferred Sales & Marketing Strategies
- 2.5.8. Key Recommendations and Analysis
- 2.5.9. A Way Forward
- 2.1. Global Food Waste Management Market Outlook
- 3. Industry Data and Premium Insights
- 3.1. Global Food & Beverages Overview, 2025
- 3.1.1. Industry Ecosystem Analysis
- 3.1.2. Key Trends for Food & Beverages Industry
- 3.1.3. Regional Distribution for Food & Beverages
- 3.2. Supplier Customer Data
- 3.3. Technology Roadmap and Developments
- 3.1. Global Food & Beverages Overview, 2025
- 4. Market Overview
- 4.1. Market Dynamics
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.1.1.1. Rising foodservice and supply chain volumes.
- 4.1.1.2. Growing environmental awareness and regulatory pressure.
- 4.1.1.3. Technological advancements in waste processing and tracking.
- 4.1.2. Restraints
- 4.1.2.1. High upfront costs and lack of infrastructure
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.2. Key Trend Analysis
- 4.3. Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1. Key Regulations, Norms, and Subsidies, by Key Countries
- 4.3.2. Tariffs and Standards
- 4.3.3. Impact Analysis of Regulations on the Market
- 4.4. Value Chain Analysis/ Ecosystem Analysis
- 4.4.1. Waste Generators
- 4.4.2. Collection & Transportation Providers
- 4.4.3. Processing & Treatment Facilities
- 4.4.4. End Users
- 4.5. Cost Structure Analysis
- 4.5.1. Parameter’s Share for Cost Associated
- 4.5.2. COGP vs COGS
- 4.5.3. Profit Margin Analysis
- 4.6. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7. PESTEL Analysis
- 4.8. Global Food Waste Management Market Demand
- 4.8.1. Historical Market Size - in Value (Value - US$ Billion), 2021-2024
- 4.8.2. Current and Future Market Size - in Value (Value - US$ Billion), 2025–2035
- 4.8.2.1. Y-o-Y Growth Trends
- 4.8.2.2. Absolute $ Opportunity Assessment
- 4.1. Market Dynamics
- 5. Competition Landscape
- 5.1. Competition structure
- 5.1.1. Fragmented v/s consolidated
- 5.2. Company Share Analysis, 2025
- 5.2.1. Global Company Market Share
- 5.2.2. By Region
- 5.2.2.1. North America
- 5.2.2.2. Europe
- 5.2.2.3. Asia Pacific
- 5.2.2.4. Middle East
- 5.2.2.5. Africa
- 5.2.2.6. South America
- 5.3. Product Comparison Matrix
- 5.3.1. Specifications
- 5.3.2. Market Positioning
- 5.3.3. Pricing
- 5.1. Competition structure
- 6. Global Food Waste Management Market Analysis, by Waste Type
- 6.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 6.2. Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Waste Type, 2021-2035
- 6.2.1. Food Production Waste
- 6.2.2. Food Processing Waste
- 6.2.3. Distribution & Supply Chain Waste
- 6.2.4. Retail Waste
- 6.2.5. Household/ Consumer-Level Waste
- 6.2.6. Post-consumer Plate Waste
- 6.2.7. Others
- 7. Global Food Waste Management Market Analysis, by Process
- 7.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 7.2. Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Process, 2021-2035
- 7.2.1. Aerobic Digestion (Composting)
- 7.2.2. Anaerobic Digestion (Biogas Production)
- 7.2.3. Incineration & Combustion
- 7.2.4. Landfilling
- 7.2.5. Fermentation
- 7.2.6. Land Application
- 7.2.7. Others
- 8. Global Food Waste Management Market Analysis, by Source
- 8.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 8.2. Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Source, 2021-2035
- 8.2.1. Residential (Households)
- 8.2.2. Commercial (Hotels, Restaurants, Catering Services)
- 8.2.3. Industrial (Food Manufacturers, Packaging & Processing Units)
- 8.2.4. Institutional (Hospitals, Schools, Government Facilities)
- 8.2.5. Retail & Supermarkets
- 8.2.6. Others
- 9. Global Food Waste Management Market Analysis, by Organization Size
- 9.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 9.2. Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Organization Size, 2021-2035
- 9.2.1. Large Enterprises
- 9.2.2. Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- 10. Global Food Waste Management Market Analysis, by Service Type
- 10.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 10.2. Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Service Type, 2021-2035
- 10.2.1. Collection & Transportation
- 10.2.2. Recycling & Composting Services
- 10.2.3. Disposal Services
- 10.2.4. Consulting & Auditing Services
- 10.2.5. Monitoring & Analytics Solutions
- 10.2.6. Others
- 11. Global Food Waste Management Market Analysis, by Treatment Method
- 11.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 11.2. Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Treatment Method, 2021-2035
- 11.2.1. Mechanical Biological Treatment (MBT)
- 11.2.2. Thermal Treatment
- 11.2.3. Biological Treatment
- 11.2.4. Physical Processing
- 11.2.5. Waste Reduction through Redistributing Edible Food
- 11.2.6. Others
- 12. Global Food Waste Management Market Analysis, by End Use
- 12.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 12.2. Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, by End Use, 2021-2035
- 12.2.1. Animal Feed
- 12.2.2. Fertilizer Production (Organic Compost)
- 12.2.3. Renewable Energy (Biogas/Biofuel)
- 12.2.4. Food Redistribution (Human Consumption)
- 12.2.5. Industrial Use (Enzymes, Chemicals)
- 12.2.6. Others
- 13. Global Food Waste Management Market Analysis and Forecasts, by Region
- 13.1. Key Findings
- 13.2. Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Region, 2021-2035
- 13.2.1. North America
- 13.2.2. Europe
- 13.2.3. Asia Pacific
- 13.2.4. Middle East
- 13.2.5. Africa
- 13.2.6. South America
- 14. North America Food Waste Management Market Analysis
- 14.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 14.2. Regional Snapshot
- 14.3. North America Food Waste Management Market Size Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 14.3.1. Waste Type
- 14.3.2. Process
- 14.3.3. Source
- 14.3.4. Organization Size
- 14.3.5. Service Type
- 14.3.6. Treatment Method
- 14.3.7. End Use
- 14.3.8. Country
- 14.3.8.1. USA
- 14.3.8.2. Canada
- 14.3.8.3. Mexico
- 14.4. USA Food Waste Management Market
- 14.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 14.4.2. Waste Type
- 14.4.3. Process
- 14.4.4. Source
- 14.4.5. Organization Size
- 14.4.6. Service Type
- 14.4.7. Treatment Method
- 14.4.8. End Use
- 14.5. Canada Food Waste Management Market
- 14.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 14.5.2. Waste Type
- 14.5.3. Process
- 14.5.4. Source
- 14.5.5. Organization Size
- 14.5.6. Service Type
- 14.5.7. Treatment Method
- 14.5.8. End Use
- 14.6. Mexico Food Waste Management Market
- 14.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 14.6.2. Waste Type
- 14.6.3. Process
- 14.6.4. Source
- 14.6.5. Organization Size
- 14.6.6. Service Type
- 14.6.7. Treatment Method
- 14.6.8. End Use
- 15. Europe Food Waste Management Market Analysis
- 15.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 15.2. Regional Snapshot
- 15.3. Europe Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 15.3.1. Waste Type
- 15.3.2. Process
- 15.3.3. Source
- 15.3.4. Organization Size
- 15.3.5. Service Type
- 15.3.6. Treatment Method
- 15.3.7. End Use
- 15.3.8. Country
- 15.3.8.1. Germany
- 15.3.8.2. United Kingdom
- 15.3.8.3. France
- 15.3.8.4. Italy
- 15.3.8.5. Spain
- 15.3.8.6. Netherlands
- 15.3.8.7. Nordic Countries
- 15.3.8.8. Poland
- 15.3.8.9. Russia & CIS
- 15.3.8.10. Rest of Europe
- 15.4. Germany Food Waste Management Market
- 15.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.4.2. Waste Type
- 15.4.3. Process
- 15.4.4. Source
- 15.4.5. Organization Size
- 15.4.6. Service Type
- 15.4.7. Treatment Method
- 15.4.8. End Use
- 15.5. United Kingdom Food Waste Management Market
- 15.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.5.2. Waste Type
- 15.5.3. Process
- 15.5.4. Source
- 15.5.5. Organization Size
- 15.5.6. Service Type
- 15.5.7. Treatment Method
- 15.5.8. End Use
- 15.6. France Food Waste Management Market
- 15.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.6.2. Waste Type
- 15.6.3. Process
- 15.6.4. Source
- 15.6.5. Organization Size
- 15.6.6. Service Type
- 15.6.7. Treatment Method
- 15.6.8. End Use
- 15.7. Italy Food Waste Management Market
- 15.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.7.2. Waste Type
- 15.7.3. Process
- 15.7.4. Source
- 15.7.5. Organization Size
- 15.7.6. Service Type
- 15.7.7. Treatment Method
- 15.7.8. End Use
- 15.8. Spain Food Waste Management Market
- 15.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.8.2. Waste Type
- 15.8.3. Process
- 15.8.4. Source
- 15.8.5. Organization Size
- 15.8.6. Service Type
- 15.8.7. Treatment Method
- 15.8.8. End Use
- 15.9. Netherlands Food Waste Management Market
- 15.9.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.9.2. Waste Type
- 15.9.3. Process
- 15.9.4. Source
- 15.9.5. Organization Size
- 15.9.6. Service Type
- 15.9.7. Treatment Method
- 15.9.8. End Use
- 15.10. Nordic Countries Food Waste Management Market
- 15.10.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.10.2. Waste Type
- 15.10.3. Process
- 15.10.4. Source
- 15.10.5. Organization Size
- 15.10.6. Service Type
- 15.10.7. Treatment Method
- 15.10.8. End Use
- 15.11. Poland Food Waste Management Market
- 15.11.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.11.2. Waste Type
- 15.11.3. Process
- 15.11.4. Source
- 15.11.5. Organization Size
- 15.11.6. Service Type
- 15.11.7. Treatment Method
- 15.11.8. End Use
- 15.12. Russia & CIS Food Waste Management Market
- 15.12.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.12.2. Waste Type
- 15.12.3. Process
- 15.12.4. Source
- 15.12.5. Organization Size
- 15.12.6. Service Type
- 15.12.7. Treatment Method
- 15.12.8. End Use
- 15.13. Rest of Europe Food Waste Management Market
- 15.13.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.13.2. Waste Type
- 15.13.3. Process
- 15.13.4. Source
- 15.13.5. Organization Size
- 15.13.6. Service Type
- 15.13.7. Treatment Method
- 15.13.8. End Use
- 16. Asia Pacific Food Waste Management Market Analysis
- 16.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 16.2. Regional Snapshot
- 16.3. East Asia Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 16.3.1. Waste Type
- 16.3.2. Process
- 16.3.3. Source
- 16.3.4. Organization Size
- 16.3.5. Service Type
- 16.3.6. Treatment Method
- 16.3.7. End Use
- 16.3.8. Country
- 16.3.8.1. China
- 16.3.8.2. India
- 16.3.8.3. Japan
- 16.3.8.4. South Korea
- 16.3.8.5. Australia and New Zealand
- 16.3.8.6. Indonesia
- 16.3.8.7. Malaysia
- 16.3.8.8. Thailand
- 16.3.8.9. Vietnam
- 16.3.8.10. Rest of Asia Pacific
- 16.4. China Food Waste Management Market
- 16.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.4.2. Waste Type
- 16.4.3. Process
- 16.4.4. Source
- 16.4.5. Organization Size
- 16.4.6. Service Type
- 16.4.7. Treatment Method
- 16.4.8. End Use
- 16.5. India Food Waste Management Market
- 16.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.5.2. Waste Type
- 16.5.3. Process
- 16.5.4. Source
- 16.5.5. Organization Size
- 16.5.6. Service Type
- 16.5.7. Treatment Method
- 16.5.8. End Use
- 16.6. Japan Food Waste Management Market
- 16.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.6.2. Waste Type
- 16.6.3. Process
- 16.6.4. Source
- 16.6.5. Organization Size
- 16.6.6. Service Type
- 16.6.7. Treatment Method
- 16.6.8. End Use
- 16.7. South Korea Food Waste Management Market
- 16.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.7.2. Waste Type
- 16.7.3. Process
- 16.7.4. Source
- 16.7.5. Organization Size
- 16.7.6. Service Type
- 16.7.7. Treatment Method
- 16.7.8. End Use
- 16.8. Australia and New Zealand Food Waste Management Market
- 16.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.8.2. Waste Type
- 16.8.3. Process
- 16.8.4. Source
- 16.8.5. Organization Size
- 16.8.6. Service Type
- 16.8.7. Treatment Method
- 16.8.8. End Use
- 16.9. Indonesia Food Waste Management Market
- 16.9.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.9.2. Waste Type
- 16.9.3. Process
- 16.9.4. Source
- 16.9.5. Organization Size
- 16.9.6. Service Type
- 16.9.7. Treatment Method
- 16.9.8. End Use
- 16.10. Malaysia Food Waste Management Market
- 16.10.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.10.2. Waste Type
- 16.10.3. Process
- 16.10.4. Source
- 16.10.5. Organization Size
- 16.10.6. Service Type
- 16.10.7. Treatment Method
- 16.10.8. End Use
- 16.11. Thailand Food Waste Management Market
- 16.11.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.11.2. Waste Type
- 16.11.3. Process
- 16.11.4. Source
- 16.11.5. Organization Size
- 16.11.6. Service Type
- 16.11.7. Treatment Method
- 16.11.8. End Use
- 16.12. Vietnam Food Waste Management Market
- 16.12.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.12.2. Waste Type
- 16.12.3. Process
- 16.12.4. Source
- 16.12.5. Organization Size
- 16.12.6. Service Type
- 16.12.7. Treatment Method
- 16.12.8. End Use
- 16.13. Rest of Asia Pacific Food Waste Management Market
- 16.13.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.13.2. Waste Type
- 16.13.3. Process
- 16.13.4. Source
- 16.13.5. Organization Size
- 16.13.6. Service Type
- 16.13.7. Treatment Method
- 16.13.8. End Use
- 17. Middle East Food Waste Management Market Analysis
- 17.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 17.2. Regional Snapshot
- 17.3. Middle East Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 17.3.1. Waste Type
- 17.3.2. Process
- 17.3.3. Source
- 17.3.4. Organization Size
- 17.3.5. Service Type
- 17.3.6. Treatment Method
- 17.3.7. End Use
- 17.3.8. Country
- 17.3.8.1. Turkey
- 17.3.8.2. UAE
- 17.3.8.3. Saudi Arabia
- 17.3.8.4. Israel
- 17.3.8.5. Rest of Middle East
- 17.4. Turkey Food Waste Management Market
- 17.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.4.2. Waste Type
- 17.4.3. Process
- 17.4.4. Source
- 17.4.5. Organization Size
- 17.4.6. Service Type
- 17.4.7. Treatment Method
- 17.4.8. End Use
- 17.5. UAE Food Waste Management Market
- 17.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.5.2. Waste Type
- 17.5.3. Process
- 17.5.4. Source
- 17.5.5. Organization Size
- 17.5.6. Service Type
- 17.5.7. Treatment Method
- 17.5.8. End Use
- 17.6. Saudi Arabia Food Waste Management Market
- 17.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.6.2. Waste Type
- 17.6.3. Process
- 17.6.4. Source
- 17.6.5. Organization Size
- 17.6.6. Service Type
- 17.6.7. Treatment Method
- 17.6.8. End Use
- 17.7. Israel Food Waste Management Market
- 17.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.7.2. Waste Type
- 17.7.3. Process
- 17.7.4. Source
- 17.7.5. Organization Size
- 17.7.6. Service Type
- 17.7.7. Treatment Method
- 17.7.8. End Use
- 17.8. Rest of Middle East Food Waste Management Market
- 17.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.8.2. Waste Type
- 17.8.3. Process
- 17.8.4. Source
- 17.8.5. Organization Size
- 17.8.6. Service Type
- 17.8.7. Treatment Method
- 17.8.8. End Use
- 18. Africa Food Waste Management Market Analysis
- 18.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 18.2. Regional Snapshot
- 18.3. Africa Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 18.3.1. Waste Type
- 18.3.2. Process
- 18.3.3. Source
- 18.3.4. Organization Size
- 18.3.5. Service Type
- 18.3.6. Treatment Method
- 18.3.7. End Use
- 18.3.8. Country
- 18.3.8.1. South Africa
- 18.3.8.2. Egypt
- 18.3.8.3. Nigeria
- 18.3.8.4. Algeria
- 18.3.8.5. Rest of Africa
- 18.4. South Africa Food Waste Management Market
- 18.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.4.2. Waste Type
- 18.4.3. Process
- 18.4.4. Source
- 18.4.5. Organization Size
- 18.4.6. Service Type
- 18.4.7. Treatment Method
- 18.4.8. End Use
- 18.5. Egypt Food Waste Management Market
- 18.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.5.2. Waste Type
- 18.5.3. Process
- 18.5.4. Source
- 18.5.5. Organization Size
- 18.5.6. Service Type
- 18.5.7. Treatment Method
- 18.5.8. End Use
- 18.6. Nigeria Food Waste Management Market
- 18.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.6.2. Waste Type
- 18.6.3. Process
- 18.6.4. Source
- 18.6.5. Organization Size
- 18.6.6. Service Type
- 18.6.7. Treatment Method
- 18.6.8. End Use
- 18.7. Algeria Food Waste Management Market
- 18.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.7.2. Waste Type
- 18.7.3. Process
- 18.7.4. Source
- 18.7.5. Organization Size
- 18.7.6. Service Type
- 18.7.7. Treatment Method
- 18.7.8. End Use
- 18.8. Rest of Africa Food Waste Management Market
- 18.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.8.2. Waste Type
- 18.8.3. Process
- 18.8.4. Source
- 18.8.5. Organization Size
- 18.8.6. Service Type
- 18.8.7. Treatment Method
- 18.8.8. End Use
- 19. South America Food Waste Management Market Analysis
- 19.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 19.2. Regional Snapshot
- 19.3. Central and South Africa Food Waste Management Market Size (Value - US$ Billion), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 19.3.1. Waste Type
- 19.3.2. Process
- 19.3.3. Source
- 19.3.4. Organization Size
- 19.3.5. Service Type
- 19.3.6. Treatment Method
- 19.3.7. End Use
- 19.3.8. Country
- 19.3.8.1. Brazil
- 19.3.8.2. Argentina
- 19.3.8.3. Rest of South America
- 19.4. Brazil Food Waste Management Market
- 19.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.4.2. Waste Type
- 19.4.3. Process
- 19.4.4. Source
- 19.4.5. Organization Size
- 19.4.6. Service Type
- 19.4.7. Treatment Method
- 19.4.8. End Use
- 19.5. Argentina Food Waste Management Market
- 19.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.5.2. Waste Type
- 19.5.3. Process
- 19.5.4. Source
- 19.5.5. Organization Size
- 19.5.6. Service Type
- 19.5.7. Treatment Method
- 19.5.8. End Use
- 19.6. Rest of South America Food Waste Management Market
- 19.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.6.2. Waste Type
- 19.6.3. Process
- 19.6.4. Source
- 19.6.5. Organization Size
- 19.6.6. Service Type
- 19.6.7. Treatment Method
- 19.6.8. End Use
- 20. Key Players/ Company Profile
- 20.1. Advanced Disposal Services, Inc.
- 20.1.1. Company Details/ Overview
- 20.1.2. Company Financials
- 20.1.3. Key Customers and Competitors
- 20.1.4. Business/ Industry Portfolio
- 20.1.5. Product Portfolio/ Specification Details
- 20.1.6. Pricing Data
- 20.1.7. Strategic Overview
- 20.1.8. Recent Developments
- 20.2. Biffa Group Limited
- 20.3. Biogen (UK)
- 20.4. BioHiTech Global, Inc.
- 20.5. Clean Harbors, Inc.
- 20.6. Covanta Holding Corporation
- 20.7. EcoSave Systems Pty Ltd.
- 20.8. FCC Environment Ltd.
- 20.9. Grind2Energy (Emerson Group)
- 20.10. Harvest Power, Inc.
- 20.11. Recology Inc.
- 20.12. Remondis SE & Co. KG
- 20.13. Republic Services, Inc.
- 20.14. Rumpke Consolidated Companies, Inc.
- 20.15. SEaB Energy Ltd.
- 20.16. Stericycle, Inc.
- 20.17. Suez S.A.
- 20.18. Veolia Environnement S.A.
- 20.19. Waste Connections, Inc.
- 20.20. Waste Management, Inc.
- 20.21. Other Key Players
- 20.1. Advanced Disposal Services, Inc.
Note* - This is just tentative list of players. While providing the report, we will cover a greater number of players based on their revenue and share for each geography
Research Design
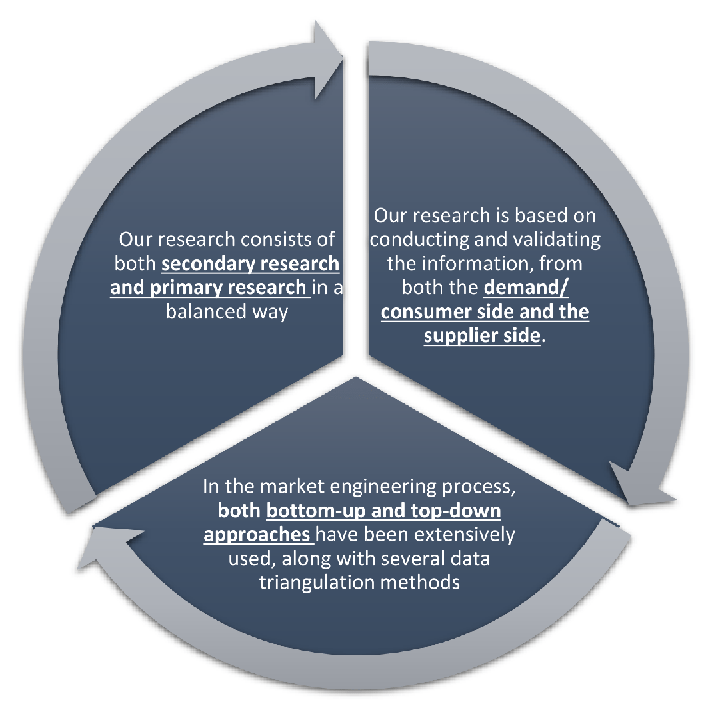
Our research design integrates both demand-side and supply-side analysis through a balanced combination of primary and secondary research methodologies. By utilizing both bottom-up and top-down approaches alongside rigorous data triangulation methods, we deliver robust market intelligence that supports strategic decision-making.
MarketGenics' comprehensive research design framework ensures the delivery of accurate, reliable, and actionable market intelligence. Through the integration of multiple research approaches, rigorous validation processes, and expert analysis, we provide our clients with the insights needed to make informed strategic decisions and capitalize on market opportunities.
MarketGenics leverages a dedicated industry panel of experts and a comprehensive suite of paid databases to effectively collect, consolidate, and analyze market intelligence.
Our approach has consistently proven to be reliable and effective in generating accurate market insights, identifying key industry trends, and uncovering emerging business opportunities.
Through both primary and secondary research, we capture and analyze critical company-level data such as manufacturing footprints, including technical centers, R&D facilities, sales offices, and headquarters.
Our expert panel further enhances our ability to estimate market size for specific brands based on validated field-level intelligence.
Our data mining techniques incorporate both parametric and non-parametric methods, allowing for structured data collection, sorting, processing, and cleaning.
Demand projections are derived from large-scale data sets analyzed through proprietary algorithms, culminating in robust and reliable market sizing.
Research Approach
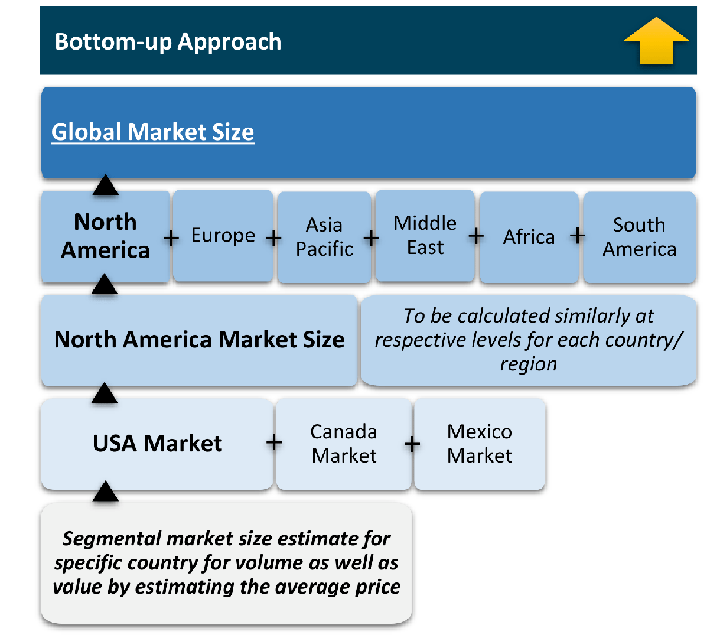
The bottom-up approach builds market estimates by starting with the smallest addressable market units and systematically aggregating them to create comprehensive market size projections.
This method begins with specific, granular data points and builds upward to create the complete market landscape.
Customer Analysis → Segmental Analysis → Geographical Analysis
The top-down approach starts with the broadest possible market data and systematically narrows it down through a series of filters and assumptions to arrive at specific market segments or opportunities.
This method begins with the big picture and works downward to increasingly specific market slices.
TAM → SAM → SOM
Research Methods
Desk / Secondary Research
While analysing the market, we extensively study secondary sources, directories, and databases to identify and collect information useful for this technical, market-oriented, and commercial report. Secondary sources that we utilize are not only the public sources, but it is a combination of Open Source, Associations, Paid Databases, MG Repository & Knowledgebase, and others.
- Company websites, annual reports, financial reports, broker reports, and investor presentations
- National government documents, statistical databases and reports
- News articles, press releases and web-casts specific to the companies operating in the market, Magazines, reports, and others
- We gather information from commercial data sources for deriving company specific data such as segmental revenue, share for geography, product revenue, and others
- Internal and external proprietary databases (industry-specific), relevant patent, and regulatory databases
- Governing Bodies, Government Organizations
- Relevant Authorities, Country-specific Associations for Industries
We also employ the model mapping approach to estimate the product level market data through the players' product portfolio
Primary Research
Primary research/ interviews is vital in analyzing the market. Most of the cases involves paid primary interviews. Primary sources include primary interviews through e-mail interactions, telephonic interviews, surveys as well as face-to-face interviews with the different stakeholders across the value chain including several industry experts.
| Type of Respondents | Number of Primaries |
|---|---|
| Tier 2/3 Suppliers | ~20 |
| Tier 1 Suppliers | ~25 |
| End-users | ~25 |
| Industry Expert/ Panel/ Consultant | ~30 |
| Total | ~100 |
MG Knowledgebase
• Repository of industry blog, newsletter and case studies
• Online platform covering detailed market reports, and company profiles
Forecasting Factors and Models
Forecasting Factors
- Historical Trends – Past market patterns, cycles, and major events that shaped how markets behave over time. Understanding past trends helps predict future behavior.
- Industry Factors – Specific characteristics of the industry like structure, regulations, and innovation cycles that affect market dynamics.
- Macroeconomic Factors – Economic conditions like GDP growth, inflation, and employment rates that affect how much money people have to spend.
- Demographic Factors – Population characteristics like age, income, and location that determine who can buy your product.
- Technology Factors – How quickly people adopt new technology and how much technology infrastructure exists.
- Regulatory Factors – Government rules, laws, and policies that can help or restrict market growth.
- Competitive Factors – Analyzing competition structure such as degree of competition and bargaining power of buyers and suppliers.
Forecasting Models / Techniques
Multiple Regression Analysis
- Identify and quantify factors that drive market changes
- Statistical modeling to establish relationships between market drivers and outcomes
Time Series Analysis – Seasonal Patterns
- Understand regular cyclical patterns in market demand
- Advanced statistical techniques to separate trend, seasonal, and irregular components
Time Series Analysis – Trend Analysis
- Identify underlying market growth patterns and momentum
- Statistical analysis of historical data to project future trends
Expert Opinion – Expert Interviews
- Gather deep industry insights and contextual understanding
- In-depth interviews with key industry stakeholders
Multi-Scenario Development
- Prepare for uncertainty by modeling different possible futures
- Creating optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely scenarios
Time Series Analysis – Moving Averages
- Sophisticated forecasting for complex time series data
- Auto-regressive integrated moving average models with seasonal components
Econometric Models
- Apply economic theory to market forecasting
- Sophisticated economic models that account for market interactions
Expert Opinion – Delphi Method
- Harness collective wisdom of industry experts
- Structured, multi-round expert consultation process
Monte Carlo Simulation
- Quantify uncertainty and probability distributions
- Thousands of simulations with varying input parameters
Research Analysis
Our research framework is built upon the fundamental principle of validating market intelligence from both demand and supply perspectives. This dual-sided approach ensures comprehensive market understanding and reduces the risk of single-source bias.
Demand-Side Analysis: We understand end-user/application behavior, preferences, and market needs along with the penetration of the product for specific application.
Supply-Side Analysis: We estimate overall market revenue, analyze the segmental share along with industry capacity, competitive landscape, and market structure.
Validation & Evaluation
Data triangulation is a validation technique that uses multiple methods, sources, or perspectives to examine the same research question, thereby increasing the credibility and reliability of research findings. In market research, triangulation serves as a quality assurance mechanism that helps identify and minimize bias, validate assumptions, and ensure accuracy in market estimates.
- Data Source Triangulation – Using multiple data sources to examine the same phenomenon
- Methodological Triangulation – Using multiple research methods to study the same research question
- Investigator Triangulation – Using multiple researchers or analysts to examine the same data
- Theoretical Triangulation – Using multiple theoretical perspectives to interpret the same data
Custom Market Research Services
We will customise the research for you, in case the report listed above does not meet your requirements.
Get 10% Free Customisation