- The global large language models (LLM) market is valued at USD 5.9 billion in 2025.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 29.5% during the forecast period of 2026 to 2035.
- The text generation and summarization segment accounts for ~32% of the global large language models (LLM) market in 2025, driven by rising demand for automated content creation and real-time information processing across industries.
- The large language models (LLM) market is growing quickly as businesses use AI-powered automation to improve decision-making, customer engagement, and productivity.
- Across various business applications, scalability, accuracy, and contextual understanding are being enhanced by developments in multimodal AI, cloud computing, and generative model fine-tuning.
- The global large-language-models-(LLM)-market is highly consolidated, with the top five players accounting for over 70% of the market share in 2025.
- In June 2025, Google DeepMind launched Gemini 2, an advanced multimodal language model capable of processing text, code, and visual information within a unified framework.
- In October 2025, Meta introduced LLaMA 3 Enterprise Edition, specifically tailored for organizations in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and legal services that require enhanced control over their data.
- Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market is likely to create the total forecasting opportunity of USD 72.5 Bn till 2035
- Asia Pacific is most attractive region, due to the fast digital transformation, the AI-driven government initiatives, and the growing cloud infrastructure.
- The growth of the large language models (LLM) market is fueled by rising enterprise deployment in industries including banking, healthcare, retail, and education for automating communication, content generation, and decision assistance. Companies are leveraging LLMs to optimize workflows, improve customer interactions, and drive analytics efficiency.
- In June 2025, Microsoft made fine-tuned LLMs available as part of its Azure OpenAI Service, providing corporate compliant, configurable LLMs and running on-premises-showing the trend of enterprises implementing LLMs into mission-critical processes.
- Growing attention to hybrid AI models and fine-tuning for domain-specific use cases (e.g., legal writings, healthcare diagnostics) is driving usage. Growth is supported by the rise of API based large language models platforms from OpenAI, Anthropic, and Cohere and existing enterprise ecosystems with built-in large language model’s integration.
- While pushing forward on the regulatory front, widespread adoption of modern identity systems is difficult due to the complexity of establishing modern identity frameworks with legacy IT systems that predominate in many organizations. Many organizations continue to use outdated databases and manual verification procedures that create friction and interoperability issues.
- Moving to decentralized or federated identity models requires significant investment in API creation, encryption infrastructure, and data governance infrastructure, particularly for public sector agencies and small financial institutions. Sustained deployment costs, together with the need for cross-jurisdictional compliance testing, hold back adoption in developing countries and with small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Balancing your need to meet very high security standards with usability and operational costs continues to be one of the key barriers to rapid adoption around the globe.
- Large language models are now evolving into more specialized (and multimodal) AI systems rather than general-purpose text models, which could open up new areas for commercialization and research. Various companies are building domain and process-specific models in finance, pharmaceuticals, law, and defense to ensure high-level precision and intelligence in context.
- For instance, IBM Research recently announced (August 2025) the launch of the Granite Code and Finance Models designed for programming and financial analytics respectively, enabling developers to use the AI assisting coding models for development and regulatory reporting with more explicit interpretability and auditability.
- Further, there is also increasing (commercialization and economic) opportunity with multimodal models which use multiple modalities of text, image, and speech understanding for improved human-computer interaction and customized human support (or human adjutant) and advanced content generation across sectors.
- A key trend in the large language model’s market is a focus on AI that is responsible and efficient, which centers on the three concepts of transparency, sustainability, and governance. Companies such as Anthropic, Google, and Meta are advancing the concepts of “Constitutional AI” and “Responsible Scaling” to help ensure models behave safely and in alignment with human values.
- Simultaneously, the rise of open-source collaboration is stoking innovation and accessibility. Frameworks like Meta’s Llama 3, and Mixtral by Mistral and Hugging Face’s open model ecosystem are leading to collaborative development while mitigating reliance on proprietary systems.
- Other emerging technologies, including parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) and GPU acceleration with systems like NVIDIA H100, are reducing costs and power use and creating a path toward scalable and sustainable deployment, signaling the next wave of change in the global large language model’s market.
- The global large language models (LLMs) market is experiencing strong growth in the text generation and summarization segment because of the rapid growth of enterprise adoption of AI-powered tools to automate content generation, customer support, and knowledge management. Leading organizations in technology, media, and finance are incorporating LLMs into their organizations to simplify workflows and reduce manual effort in developing reports, articles, and communications. For example, Microsoft and OpenAI expanded their collaboration in 2025 to deploy GPT-based models throughout Microsoft 365, improving document summarization and automating business insights.
- The integration of advanced transformer architectures and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has greatly improved the contextual accuracy and coherence of generated texts. Companies like Anthropic, Cohere, and Google DeepMind are building domain-specific LLMs that have been fine-tuned for summarization and automation of documents around a specific industry to address healthcare, law, and finance needs.
- Regulatory and compliance requirements are driving enterprise adoption of AI summarization systems to demonstrate consistency, auditability, and knowledge retention. In addition, cloud-native application programming interfaces (APIs) for LLMs, as well as open-source frameworks from Hugging Face and NVIDIA, are enabling developers to deploy generative text systems capable of scaling and being secure within the enterprise ecosystem, supporting the segment's global leadership.
- The Asia-Pacific region is becoming the fastest-growing market for large language models (LLMs) globally, which is a result of the fast digital transformation, the AI-driven government initiatives, and the growing cloud infrastructure. The China, Japan, South Korea, and India are the country’s leading in AI adoption across sectors like banking, manufacturing, and public services. The pervasive deployment of LLMs in localized apps such as multilingual customer support, intelligent automation, and content generation is, therefore, a major factor that drives regional demand.
- In 2025, a number of major technology companies such as Baidu, Alibaba Cloud, Huawei, and Naver AI Lab have rolled out region-specific LLMs that are language and culturally sensitive. These models are being incorporated into enterprise platforms for education, e-commerce, and smart city management. The strategic collaborations between global providers like Google Cloud and local governments are spreading the AI skills and making the technology more accessible in the developing economies.
- The national AI strategies like China’s “New Generation AI Development Plan” and India’s “National AI Mission”, coupled with aggressive cloud investments and increasing digital literacy, have set the Asia-Pacific region to become a major center for large language model innovation and application.
- In June 2025, Google DeepMind launched Gemini 2, an advanced multimodal language model capable of processing text, code, and visual information within a unified framework. Compared to its predecessor, Gemini 2 demonstrates a 23% improvement in contextual accuracy. As a result, research teams have widely adopted the model for applications ranging from complex data analysis to the automation of extensive documentation tasks.
- In October 2025, Meta introduced LLaMA 3 Enterprise Edition, specifically tailored for organizations in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and legal services that require enhanced control over their data. This solution allows enterprises to deploy the model on their own infrastructure and customize it to meet specific operational needs, thereby ensuring greater privacy and reducing the risks associated with cloud-based data storage. Additionally, LLaMA 3 Enterprise Edition lowers inference costs by nearly 33% compared to traditional cloud-based alternatives, offering a compelling value proposition for enterprise adoption.
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Nordic Countries
- Poland
- Russia & CIS
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia and New Zealand
- Indonesia
- Malaysia
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Turkey
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- Israel
- South Africa
- Egypt
- Nigeria
- Algeria
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Adept AI Labs
- Alibaba Cloud
- NVIDIA Corporation
- Amazon Web Services, Inc.
- Anthropic PBC
- AI21 Labs Ltd.
- Cerebras Systems, Inc.
- Cohere Inc.
- Databricks, Inc.
- OpenAI
- Google DeepMind
- Hugging Face, Inc.
- IBM Corporation
- Baidu, Inc.
- Meta Platforms, Inc.
- Microsoft Corporation
- Mistral AI
- Replit, Inc.
- Stability AI Ltd.
- Tencent Holdings Ltd.
- Others Key Players
- Solutions
- Pre-trained Foundation Models
- Custom LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS Development Platforms
- Model Fine-tuning and Adaptation Tools
- Model Training and Optimization Software
- API and SDK Access Platforms
- Data Preparation and Annotation Tools
- LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS Hosting and Inference Platforms
- Model Monitoring and Governance Tools
- Prompt Engineering and Workflow Automation Solutions
- Multimodal LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS Integration Tools
- Others
- Services
- Consulting Services
- LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS Strategy and Architecture Consulting
- Model Selection and Customization Guidance
- Compliance and Responsible AI Advisory
- Others
- Integration & Deployment
- Cloud and On-Premise Implementation
- API Integration with Enterprise Applications
- Fine-tuning and Model Deployment Support
- Others
- Support & Maintenance
- Continuous Model Updates and Version Management
- Performance Monitoring and Optimization
- Technical Support and Security Management
- Others
- On-Premises
- Cloud-Based
- Hybrid
- GPT-based Models
- BERT-based Models
- Transformer-based Models
- T5 Models
- LLaMA Models
- BLOOM Models
- Custom Proprietary LLMs
- Others
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
- Few-shot and Zero-shot Learning
- Others
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- Large Enterprises
- Research and Development
- Customer Support Automation
- Product Design and Innovation
- Risk and Compliance Management
- Others
- Text Generation and Summarization
- Conversational AI and Chatbots
- Code Generation
- Content Creation and Copywriting
- Sentiment Analysis
- Translation and Localization
- Knowledge Management
- Virtual Assistants
- Others
- IT and Telecommunications
- BFSI
- Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Retail and E-commerce
- Media and Entertainment
- Education
- Government and Public Sector
- Manufacturing
- Others
- 1. Research Methodology and Assumptions
- 1.1. Definitions
- 1.2. Research Design and Approach
- 1.3. Data Collection Methods
- 1.4. Base Estimates and Calculations
- 1.5. Forecasting Models
- 1.5.1. Key Forecast Factors & Impact Analysis
- 1.6. Secondary Research
- 1.6.1. Open Sources
- 1.6.2. Paid Databases
- 1.6.3. Associations
- 1.7. Primary Research
- 1.7.1. Primary Sources
- 1.7.2. Primary Interviews with Stakeholders across Ecosystem
- 2. Executive Summary
- 2.1. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Outlook
- 2.1.1. Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 2.1.2. Compounded Annual Growth Rate Analysis
- 2.1.3. Growth Opportunity Analysis
- 2.1.4. Segmental Share Analysis
- 2.1.5. Geographical Share Analysis
- 2.2. Market Analysis and Facts
- 2.3. Supply-Demand Analysis
- 2.4. Competitive Benchmarking
- 2.5. Go-to- Market Strategy
- 2.5.1. Customer/ End-use Industry Assessment
- 2.5.2. Growth Opportunity Data, 2026-2035
- 2.5.2.1. Regional Data
- 2.5.2.2. Country Data
- 2.5.2.3. Segmental Data
- 2.5.3. Identification of Potential Market Spaces
- 2.5.4. GAP Analysis
- 2.5.5. Potential Attractive Price Points
- 2.5.6. Prevailing Market Risks & Challenges
- 2.5.7. Preferred Sales & Marketing Strategies
- 2.5.8. Key Recommendations and Analysis
- 2.5.9. A Way Forward
- 2.1. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Outlook
- 3. Industry Data and Premium Insights
- 3.1. Global Information Technology & Media Ecosystem Overview, 2025
- 3.1.1. Information Technology & Media Industry Analysis
- 3.1.2. Key Trends for Information Technology & Media Industry
- 3.1.3. Regional Distribution for Information Technology & Media Industry
- 3.2. Supplier Customer Data
- 3.3. Technology Roadmap and Developments
- 3.1. Global Information Technology & Media Ecosystem Overview, 2025
- 4. Market Overview
- 4.1. Market Dynamics
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.1.1.1. Rising demand for AI-driven content generation and real-time text analysis
- 4.1.1.2. Growing adoption of conversational AI, chatbots, and virtual assistants across industries
- 4.1.1.3. Increasing regulatory focus on AI transparency, data privacy, and ethical model usage
- 4.1.2. Restraints
- 4.1.2.1. High development and deployment costs of advanced large language models
- 4.1.2.2. Challenges in integrating large language models with legacy systems and existing enterprise workflows
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.2. Key Trend Analysis
- 4.3. Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1. Key Regulations, Norms, and Subsidies, by Key Countries
- 4.3.2. Tariffs and Standards
- 4.3.3. Impact Analysis of Regulations on the Market
- 4.4. Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4.1. Data Providers
- 4.4.2. System Integrators/ Technology Providers
- 4.4.3. LLM Solution Providers
- 4.4.4. End Users
- 4.5. Cost Structure Analysis
- 4.5.1. Parameter’s Share for Cost Associated
- 4.5.2. COGP vs COGS
- 4.5.3. Profit Margin Analysis
- 4.6. Pricing Analysis
- 4.6.1. Regional Pricing Analysis
- 4.6.2. Segmental Pricing Trends
- 4.6.3. Factors Influencing Pricing
- 4.7. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8. PESTEL Analysis
- 4.9. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Demand
- 4.9.1. Historical Market Size –Value (US$ Bn), 2020-2024
- 4.9.2. Current and Future Market Size –Value (US$ Bn), 2026–2035
- 4.9.2.1. Y-o-Y Growth Trends
- 4.9.2.2. Absolute $ Opportunity Assessment
- 4.1. Market Dynamics
- 5. Competition Landscape
- 5.1. Competition structure
- 5.1.1. Fragmented v/s consolidated
- 5.2. Company Share Analysis, 2025
- 5.2.1. Global Company Market Share
- 5.2.2. By Region
- 5.2.2.1. North America
- 5.2.2.2. Europe
- 5.2.2.3. Asia Pacific
- 5.2.2.4. Middle East
- 5.2.2.5. Africa
- 5.2.2.6. South America
- 5.3. Product Comparison Matrix
- 5.3.1. Specifications
- 5.3.2. Market Positioning
- 5.3.3. Pricing
- 5.1. Competition structure
- 6. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis, by Component
- 6.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 6.2. Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Component, 2021-2035
- 6.2.1. Solutions
- 6.2.1.1. Pre-trained Foundation Models
- 6.2.1.2. Custom LLM Development Platforms
- 6.2.1.3. Model Fine-tuning and Adaptation Tools
- 6.2.1.4. Model Training and Optimization Software
- 6.2.1.5. API and SDK Access Platforms
- 6.2.1.6. Data Preparation and Annotation Tools
- 6.2.1.7. LLM Hosting and Inference Platforms
- 6.2.1.8. Model Monitoring and Governance Tools
- 6.2.1.9. Prompt Engineering and Workflow Automation Solutions
- 6.2.1.10. Multimodal LLM Integration Tools
- 6.2.1.11. Others
- 6.2.2. Services
- 6.2.2.1. Consulting Services
- 6.2.2.1.1. LLM Strategy and Architecture Consulting
- 6.2.2.1.2. Model Selection and Customization Guidance
- 6.2.2.1.3. Compliance and Responsible AI Advisory
- 6.2.2.1.4. Others
- 6.2.2.2. Integration & Deployment
- 6.2.2.2.1. Cloud and On-Premise Implementation
- 6.2.2.2.2. API Integration with Enterprise Applications
- 6.2.2.2.3. Fine-tuning and Model Deployment Support
- 6.2.2.2.4. Others
- 6.2.2.3. Support & Maintenance
- 6.2.2.3.1. Continuous Model Updates and Version Management
- 6.2.2.3.2. Performance Monitoring and Optimization
- 6.2.2.3.3. Technical Support and Security Management
- 6.2.2.3.4. Others
- 6.2.2.1. Consulting Services
- 6.2.1. Solutions
- 7. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis, by Deployment Mode
- 7.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 7.2. Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Deployment Mode, 2021-2035
- 7.2.1. Cloud-Based
- 7.2.2. On-Premises
- 7.2.3. Hybrid
- 8. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis, by Model Type
- 8.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 8.2. Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Model Type, 2021-2035
- 8.2.1. GPT-based Models
- 8.2.2. BERT-based Models
- 8.2.3. Transformer-based Models
- 8.2.4. T5 Models
- 8.2.5. LLaMA Models
- 8.2.6. BLOOM Models
- 8.2.7. Custom Proprietary LLMs
- 8.2.8. Others
- 9. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis, by Training Approach
- 9.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 9.2. Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Training Approach, 2021-2035
- 9.2.1. Supervised Learning
- 9.2.2. Unsupervised Learning
- 9.2.3. Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
- 9.2.4. Few-shot and Zero-shot Learning
- 9.2.5. Others
- 10. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis, by Enterprise Size
- 10.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 10.2. Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Enterprise Size, 2021-2035
- 10.2.1. Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- 10.2.2. Large Enterprises
- 11. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis, by Function
- 11.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 11.2. Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Function, 2021-2035
- 11.2.1. Research and Development
- 11.2.2. Customer Support Automation
- 11.2.3. Product Design and Innovation
- 11.2.4. Risk and Compliance Management
- 11.2.5. Others
- 12. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis, by Application
- 12.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 12.2. Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Application, 2021-2035
- 12.2.1. Text Generation and Summarization
- 12.2.2. Conversational AI and Chatbots
- 12.2.3. Code Generation
- 12.2.4. Content Creation and Copywriting
- 12.2.5. Sentiment Analysis
- 12.2.6. Translation and Localization
- 12.2.7. Knowledge Management
- 12.2.8. Virtual Assistants
- 12.2.9. Others
- 13. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis, by Industry Vertical
- 13.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 13.2. Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Industry Vertical, 2021-2035
- 13.2.1. IT and Telecommunications
- 13.2.2. BFSI
- 13.2.3. Healthcare and Life Sciences
- 13.2.4. Retail and E-commerce
- 13.2.5. Media and Entertainment
- 13.2.6. Education
- 13.2.7. Government and Public Sector
- 13.2.8. Manufacturing
- 13.2.9. Others
- 14. Global Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis and Forecasts, by Region
- 14.1. Key Findings
- 14.2. Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Region, 2021-2035
- 14.2.1. North America
- 14.2.2. Europe
- 14.2.3. Asia Pacific
- 14.2.4. Middle East
- 14.2.5. Africa
- 14.2.6. South America
- 15. North America Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis
- 15.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 15.2. Regional Snapshot
- 15.3. North America Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 15.3.1. Component
- 15.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 15.3.3. Model Type
- 15.3.4. Deployment Type
- 15.3.5. Training Approach
- 15.3.6. Enterprise Size
- 15.3.7. Function
- 15.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 15.3.9. Country
- 15.3.9.1. USA
- 15.3.9.2. Canada
- 15.3.9.3. Mexico
- 15.4. USA Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 15.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.4.2. Component
- 15.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 15.4.4. Model Type
- 15.4.5. Deployment Type
- 15.4.6. Training Approach
- 15.4.7. Enterprise Size
- 15.4.8. Function
- 15.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 15.5. Canada Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 15.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.5.2. Component
- 15.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 15.5.4. Model Type
- 15.5.5. Deployment Type
- 15.5.6. Training Approach
- 15.5.7. Enterprise Size
- 15.5.8. Function
- 15.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 15.6. Mexico Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 15.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.6.2. Component
- 15.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 15.6.4. Model Type
- 15.6.5. Deployment Type
- 15.6.6. Training Approach
- 15.6.7. Enterprise Size
- 15.6.8. Function
- 15.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 16. Europe Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis
- 16.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 16.2. Regional Snapshot
- 16.3. Europe Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 16.3.1. Component
- 16.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 16.3.3. Model Type
- 16.3.4. Deployment Type
- 16.3.5. Training Approach
- 16.3.6. Enterprise Size
- 16.3.7. Function
- 16.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 16.3.9. Country
- 16.3.9.1. Germany
- 16.3.9.2. United Kingdom
- 16.3.9.3. France
- 16.3.9.4. Italy
- 16.3.9.5. Spain
- 16.3.9.6. Netherlands
- 16.3.9.7. Nordic Countries
- 16.3.9.8. Poland
- 16.3.9.9. Russia & CIS
- 16.3.9.10. Rest of Europe
- 16.4. Germany Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 16.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.4.2. Component
- 16.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.4.4. Model Type
- 16.4.5. Deployment Type
- 16.4.6. Training Approach
- 16.4.7. Enterprise Size
- 16.4.8. Function
- 16.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.5. United Kingdom Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 16.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.5.2. Component
- 16.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.5.4. Model Type
- 16.5.5. Deployment Type
- 16.5.6. Training Approach
- 16.5.7. Enterprise Size
- 16.5.8. Function
- 16.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.6. France Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 16.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.6.2. Component
- 16.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.6.4. Model Type
- 16.6.5. Deployment Type
- 16.6.6. Training Approach
- 16.6.7. Enterprise Size
- 16.6.8. Function
- 16.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.7. Italy Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 16.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.7.2. Component
- 16.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.7.4. Model Type
- 16.7.5. Deployment Type
- 16.7.6. Training Approach
- 16.7.7. Enterprise Size
- 16.7.8. Function
- 16.7.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.8. Spain Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 16.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.8.2. Component
- 16.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.8.4. Model Type
- 16.8.5. Deployment Type
- 16.8.6. Training Approach
- 16.8.7. Enterprise Size
- 16.8.8. Function
- 16.8.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.9. Netherlands Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 16.9.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.9.2. Component
- 16.9.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.9.4. Model Type
- 16.9.5. Deployment Type
- 16.9.6. Training Approach
- 16.9.7. Enterprise Size
- 16.9.8. Function
- 16.9.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.10. Nordic Countries Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 16.10.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.10.2. Component
- 16.10.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.10.4. Model Type
- 16.10.5. Deployment Type
- 16.10.6. Training Approach
- 16.10.7. Enterprise Size
- 16.10.8. Function
- 16.10.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.11. Poland Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 16.11.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.11.2. Component
- 16.11.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.11.4. Model Type
- 16.11.5. Deployment Type
- 16.11.6. Training Approach
- 16.11.7. Enterprise Size
- 16.11.8. Function
- 16.11.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.12. Russia & CIS Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 16.12.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.12.2. Component
- 16.12.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.12.4. Model Type
- 16.12.5. Deployment Type
- 16.12.6. Training Approach
- 16.12.7. Enterprise Size
- 16.12.8. Function
- 16.12.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.13. Rest of Europe Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 16.13.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.13.2. Component
- 16.13.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.13.4. Model Type
- 16.13.5. Deployment Type
- 16.13.6. Training Approach
- 16.13.7. Enterprise Size
- 16.13.8. Function
- 16.13.9. Industry Vertical
- 17. Asia Pacific Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis
- 17.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 17.2. Regional Snapshot
- 17.3. Asia Pacific Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 17.3.1. Component
- 17.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 17.3.3. Model Type
- 17.3.4. Deployment Type
- 17.3.5. Training Approach
- 17.3.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.3.7. Function
- 17.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 17.3.9. Country
- 17.3.9.1. China
- 17.3.9.2. India
- 17.3.9.3. Japan
- 17.3.9.4. South Korea
- 17.3.9.5. Australia and New Zealand
- 17.3.9.6. Indonesia
- 17.3.9.7. Malaysia
- 17.3.9.8. Thailand
- 17.3.9.9. Vietnam
- 17.3.9.10. Rest of Asia Pacific
- 17.4. China Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 17.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.4.2. Component
- 17.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.4.4. Model Type
- 17.4.5. Deployment Type
- 17.4.6. Training Approach
- 17.4.7. Enterprise Size
- 17.4.8. Function
- 17.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.5. India Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 17.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.5.2. Component
- 17.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.5.4. Model Type
- 17.5.5. Deployment Type
- 17.5.6. Training Approach
- 17.5.7. Enterprise Size
- 17.5.8. Function
- 17.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.6. Japan Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 17.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.6.2. Component
- 17.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.6.4. Model Type
- 17.6.5. Deployment Type
- 17.6.6. Training Approach
- 17.6.7. Enterprise Size
- 17.6.8. Function
- 17.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.7. South Korea Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 17.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.7.2. Component
- 17.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.7.4. Model Type
- 17.7.5. Deployment Type
- 17.7.6. Training Approach
- 17.7.7. Enterprise Size
- 17.7.8. Function
- 17.7.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.8. Australia and New Zealand Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 17.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.8.2. Component
- 17.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.8.4. Model Type
- 17.8.5. Deployment Type
- 17.8.6. Training Approach
- 17.8.7. Enterprise Size
- 17.8.8. Function
- 17.8.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.9. Indonesia Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 17.9.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.9.2. Component
- 17.9.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.9.4. Model Type
- 17.9.5. Deployment Type
- 17.9.6. Training Approach
- 17.9.7. Enterprise Size
- 17.9.8. Function
- 17.9.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.10. Malaysia Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 17.10.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.10.2. Component
- 17.10.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.10.4. Model Type
- 17.10.5. Deployment Type
- 17.10.6. Training Approach
- 17.10.7. Enterprise Size
- 17.10.8. Function
- 17.10.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.11. Thailand Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 17.11.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.11.2. Component
- 17.11.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.11.4. Model Type
- 17.11.5. Deployment Type
- 17.11.6. Training Approach
- 17.11.7. Enterprise Size
- 17.11.8. Function
- 17.11.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.12. Vietnam Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 17.12.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.12.2. Component
- 17.12.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.12.4. Model Type
- 17.12.5. Deployment Type
- 17.12.6. Training Approach
- 17.12.7. Enterprise Size
- 17.12.8. Function
- 17.12.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.13. Rest of Asia Pacific Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 17.13.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.13.2. Component
- 17.13.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.13.4. Model Type
- 17.13.5. Deployment Type
- 17.13.6. Training Approach
- 17.13.7. Enterprise Size
- 17.13.8. Function
- 17.13.9. Industry Vertical
- 18. Middle East Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis
- 18.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 18.2. Regional Snapshot
- 18.3. Middle East Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 18.3.1. Component
- 18.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 18.3.3. Model Type
- 18.3.4. Deployment Type
- 18.3.5. Training Approach
- 18.3.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.3.7. Function
- 18.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 18.3.9. Country
- 18.3.9.1. Turkey
- 18.3.9.2. UAE
- 18.3.9.3. Saudi Arabia
- 18.3.9.4. Israel
- 18.3.9.5. Rest of Middle East
- 18.4. Turkey Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 18.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.4.2. Component
- 18.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.4.4. Model Type
- 18.4.5. Deployment Type
- 18.4.6. Training Approach
- 18.4.7. Enterprise Size
- 18.4.8. Function
- 18.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 18.5. UAE Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 18.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.5.2. Component
- 18.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.5.4. Model Type
- 18.5.5. Deployment Type
- 18.5.6. Training Approach
- 18.5.7. Enterprise Size
- 18.5.8. Function
- 18.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 18.6. Saudi Arabia Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 18.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.6.2. Component
- 18.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.6.4. Model Type
- 18.6.5. Deployment Type
- 18.6.6. Training Approach
- 18.6.7. Enterprise Size
- 18.6.8. Function
- 18.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 18.7. Israel Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 18.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.7.2. Component
- 18.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.7.4. Model Type
- 18.7.5. Deployment Type
- 18.7.6. Training Approach
- 18.7.7. Enterprise Size
- 18.7.8. Function
- 18.7.9. Industry Vertical
- 18.8. Rest of Middle East Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 18.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.8.2. Component
- 18.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.8.4. Model Type
- 18.8.5. Deployment Type
- 18.8.6. Training Approach
- 18.8.7. Enterprise Size
- 18.8.8. Function
- 18.8.9. Industry Vertical
- 19. Africa Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis
- 19.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 19.2. Regional Snapshot
- 19.3. Africa Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 19.3.1. Component
- 19.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 19.3.3. Model Type
- 19.3.4. Deployment Type
- 19.3.5. Training Approach
- 19.3.6. Enterprise Size
- 19.3.7. Function
- 19.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 19.3.9. Country
- 19.3.9.1. South Africa
- 19.3.9.2. Egypt
- 19.3.9.3. Nigeria
- 19.3.9.4. Algeria
- 19.3.9.5. Rest of Africa
- 19.4. South Africa Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 19.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.4.2. Component
- 19.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.4.4. Model Type
- 19.4.5. Deployment Type
- 19.4.6. Training Approach
- 19.4.7. Enterprise Size
- 19.4.8. Function
- 19.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 19.5. Egypt Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 19.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.5.2. Component
- 19.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.5.4. Model Type
- 19.5.5. Deployment Type
- 19.5.6. Training Approach
- 19.5.7. Enterprise Size
- 19.5.8. Function
- 19.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 19.6. Nigeria Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 19.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.6.2. Component
- 19.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.6.4. Model Type
- 19.6.5. Deployment Type
- 19.6.6. Training Approach
- 19.6.7. Enterprise Size
- 19.6.8. Function
- 19.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 19.7. Algeria Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 19.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.7.2. Component
- 19.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.7.4. Model Type
- 19.7.5. Deployment Type
- 19.7.6. Training Approach
- 19.7.7. Enterprise Size
- 19.7.8. Function
- 19.7.9. Industry Vertical
- 19.8. Rest of Africa Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 19.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.8.2. Component
- 19.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.8.4. Model Type
- 19.8.5. Deployment Type
- 19.8.6. Training Approach
- 19.8.7. Enterprise Size
- 19.8.8. Function
- 19.8.9. Industry Vertical
- 20. South America Large Language Models (LLM) Market Analysis
- 20.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 20.2. Regional Snapshot
- 20.3. South America Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 20.3.1. Component
- 20.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 20.3.3. Model Type
- 20.3.4. Deployment Type
- 20.3.5. Training Approach
- 20.3.6. Enterprise Size
- 20.3.7. Function
- 20.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 20.3.9. Country
- 20.3.9.1. Brazil
- 20.3.9.2. Argentina
- 20.3.9.3. Rest of South America
- 20.4. Brazil Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 20.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.4.2. Component
- 20.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.4.4. Model Type
- 20.4.5. Deployment Type
- 20.4.6. Training Approach
- 20.4.7. Enterprise Size
- 20.4.8. Function
- 20.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 20.5. Argentina Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 20.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.5.2. Component
- 20.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.5.4. Model Type
- 20.5.5. Deployment Type
- 20.5.6. Training Approach
- 20.5.7. Enterprise Size
- 20.5.8. Function
- 20.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 20.6. Rest of South America Large Language Models (LLM) Market
- 20.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.6.2. Component
- 20.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.6.4. Model Type
- 20.6.5. Deployment Type
- 20.6.6. Training Approach
- 20.6.7. Enterprise Size
- 20.6.8. Function
- 20.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 21. Key Players/ Company Profile
- 21.1. Adept AI Labs
- 21.1.1. Company Details/ Overview
- 21.1.2. Company Financials
- 21.1.3. Key Customers and Competitors
- 21.1.4. Business/ Industry Portfolio
- 21.1.5. Product Portfolio/ Specification Details
- 21.1.6. Pricing Data
- 21.1.7. Strategic Overview
- 21.1.8. Recent Developments
- 21.2. AI21 Labs Ltd.
- 21.3. Alibaba Cloud
- 21.4. Amazon Web Services, Inc.
- 21.5. Anthropic PBC
- 21.6. Baidu, Inc.
- 21.7. Cerebras Systems, Inc.
- 21.8. Cohere Inc.
- 21.9. Databricks, Inc.
- 21.10. Google DeepMind
- 21.11. Hugging Face, Inc.
- 21.12. IBM Corporation
- 21.13. Meta Platforms, Inc.
- 21.14. Microsoft Corporation
- 21.15. Mistral AI
- 21.16. NVIDIA Corporation
- 21.17. OpenAI
- 21.18. Replit, Inc.
- 21.19. Stability AI Ltd.
- 21.20. Tencent Holdings Ltd.
- 21.21. Others Key Players
- 21.1. Adept AI Labs
- Company websites, annual reports, financial reports, broker reports, and investor presentations
- National government documents, statistical databases and reports
- News articles, press releases and web-casts specific to the companies operating in the market, Magazines, reports, and others
- We gather information from commercial data sources for deriving company specific data such as segmental revenue, share for geography, product revenue, and others
- Internal and external proprietary databases (industry-specific), relevant patent, and regulatory databases
- Governing Bodies, Government Organizations
- Relevant Authorities, Country-specific Associations for Industries
- Historical Trends – Past market patterns, cycles, and major events that shaped how markets behave over time. Understanding past trends helps predict future behavior.
- Industry Factors – Specific characteristics of the industry like structure, regulations, and innovation cycles that affect market dynamics.
- Macroeconomic Factors – Economic conditions like GDP growth, inflation, and employment rates that affect how much money people have to spend.
- Demographic Factors – Population characteristics like age, income, and location that determine who can buy your product.
- Technology Factors – How quickly people adopt new technology and how much technology infrastructure exists.
- Regulatory Factors – Government rules, laws, and policies that can help or restrict market growth.
- Competitive Factors – Analyzing competition structure such as degree of competition and bargaining power of buyers and suppliers.
- Identify and quantify factors that drive market changes
- Statistical modeling to establish relationships between market drivers and outcomes
- Understand regular cyclical patterns in market demand
- Advanced statistical techniques to separate trend, seasonal, and irregular components
- Identify underlying market growth patterns and momentum
- Statistical analysis of historical data to project future trends
- Gather deep industry insights and contextual understanding
- In-depth interviews with key industry stakeholders
- Prepare for uncertainty by modeling different possible futures
- Creating optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely scenarios
- Sophisticated forecasting for complex time series data
- Auto-regressive integrated moving average models with seasonal components
- Apply economic theory to market forecasting
- Sophisticated economic models that account for market interactions
- Harness collective wisdom of industry experts
- Structured, multi-round expert consultation process
- Quantify uncertainty and probability distributions
- Thousands of simulations with varying input parameters
- Data Source Triangulation – Using multiple data sources to examine the same phenomenon
- Methodological Triangulation – Using multiple research methods to study the same research question
- Investigator Triangulation – Using multiple researchers or analysts to examine the same data
- Theoretical Triangulation – Using multiple theoretical perspectives to interpret the same data
Insightified
Mid-to-large firms spend $20K–$40K quarterly on systematic research and typically recover multiples through improved growth and profitability
Research is no longer optional. Leading firms use it to uncover $10M+ in hidden revenue opportunities annually
Our research-consulting programs yields measurable ROI: 20–30% revenue increases from new markets, 11% profit upticks from pricing, and 20–30% cost savings from operations
Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Component (Solutions, Services and Platforms), Deployment Mode, Model Type, Training Approach, Enterprise Size, Function, Application, Industry Vertical and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, Africa, and South America) – Global Industry Data, Trends, and Forecasts, 2026–2035
|
Market Structure & Evolution |
|
|
Segmental Data Insights |
|
|
Demand Trends |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Strategic Development |
|
|
Future Outlook & Opportunities |
|
Large Language Models (LLM) Market Size, Share, and Growth
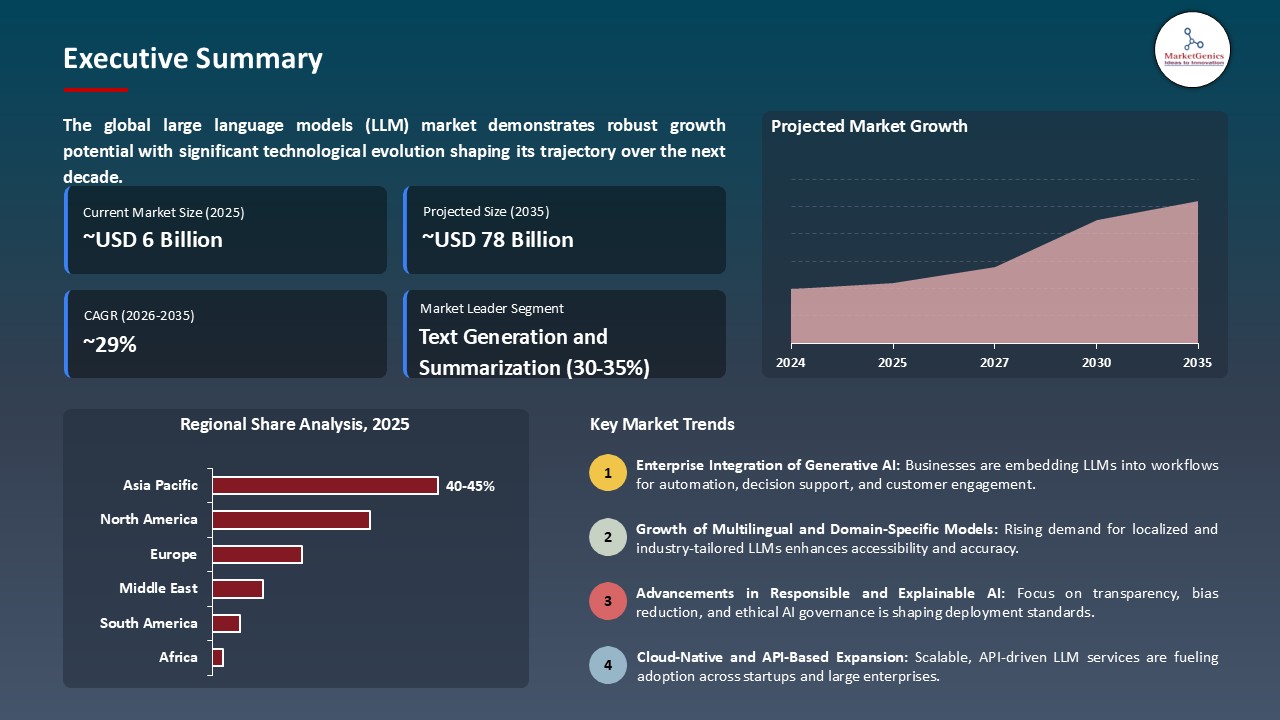
The global large language models (LLM) market is experiencing robust growth, with its estimated value of USD 5.9 billion in the year 2025 and USD 78.5 billion by the period 2035, registering a CAGR of 29.5% during the forecast period. The large language models (LLM) market is undergoing significant expansion globally as innovations, enterprise adoption and advancements in computing infrastructure continue to be an accelerating factor.
"Identity is security," said Todd McKinnon, co-founder and CEO of Okta. He stressed that identity systems must have connectivity into an organization’s security stack in order to prevent breaches and maintain zero trust resiliency. He further elaborated that as digital interactions proliferate across cloud and AI environments, the identity will still be the underpinning of secure access that protects enterprises and users against increasing levels of cyber malignancy”.
The large language models exponential development of highly capable and efficient LLMs is accelerating automation, data analysis, and content generation across industries. An illustrative example, Google DeepMind recently revealed its next-generation Gemini 2 model in July 2025, which achieves new levels of multi-modal reasoning and code-generation capabilities that increase enterprise decision-making and productivity. Similarly, OpenAI launched GPT-5 in May 2025 with features that support improved reliability, compliance and contextual accuracy for organizational environments with verifiable outputs and adaptive fine-tuning.
Heightened interest in AI-driven business intelligence, content creation and conversational automation is contributing to large language models adoption across the finance and healthcare sectors and even government. Additionally, governments developing strong data governance standards and efforts like the EU AI Act offer incentives for research and development of explainable and safe AI systems. Model optimization for proactive litigation risk for regulatory compliance and employee productivity visibly reflects the value of enterprise digital transformation. These factors are producing a profound large language models (LLM) market expansion and widening profit margins, increasing operational efficiency and trust, and reducing information-processing time.
The global large language models (LLM) market presents adjacent opportunities in the market for verification frameworks for AI integrity, synthetic data creation, edge-based inference systems, personalized AI agents, and enterprise productivity agents. Tapping into the adjacent space will allow vendors to diversify offerings, better scalability, and increased relevance in the developing intelligent automation market.
Large Language Models (LLM) Market Dynamics and Trends
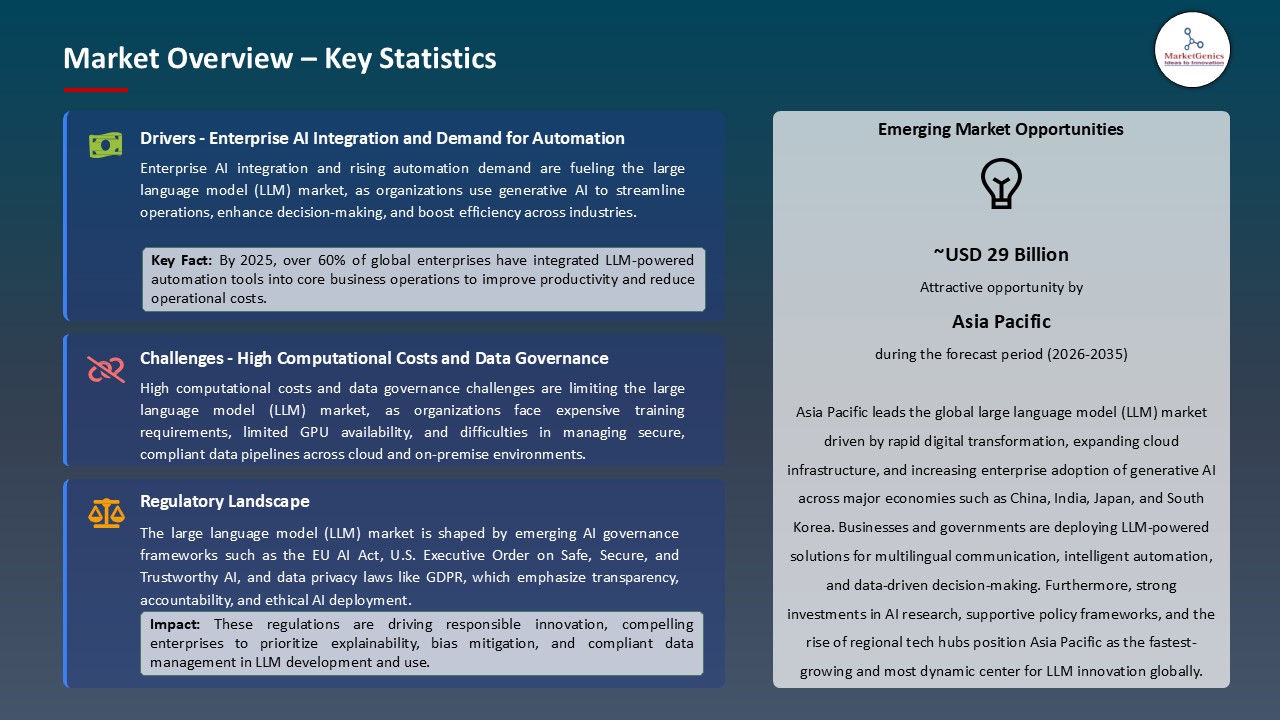
Driver: Expanding Enterprise AI Integration and Demand for Automation
Restraint: High Computational Costs and Data Governance Challenges Limiting Large Language Models (LLM) Adoption
Opportunity: Development of Domain-Specific and Multimodal Large Language Models
Key Trend: Emphasis on Responsible AI, Efficiency, and Open-Source Collaboration Boosting Large Language Models (LLM) Industry
Large Language Models Market Analysis and Segmental Data
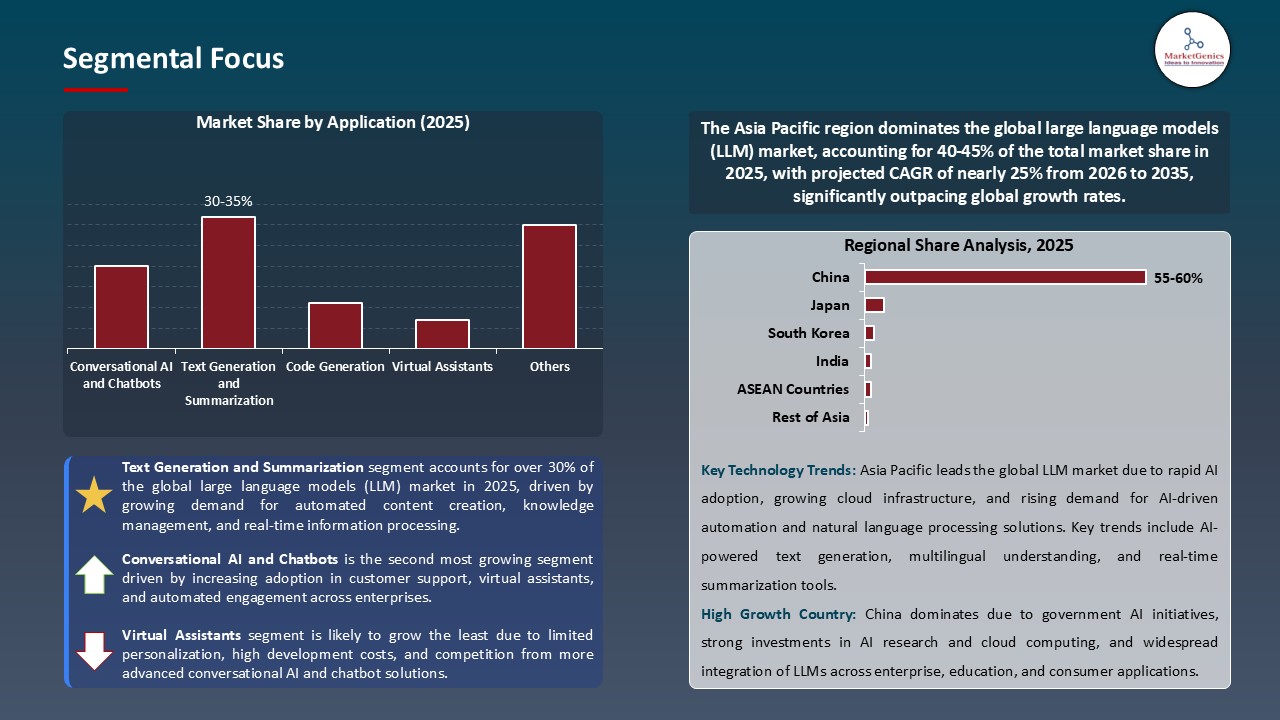
Text Generation and Summarization Segment Dominates Global Market amid Rising Demand for Intelligent Content Automation and Enterprise Knowledge Management
Asia Pacific Leads Large Language Models (LLM) Market with Rapid AI Adoption and Expanding Cloud Infrastructure
Large-Language-Models-Market Ecosystem
The global large language models (LLMs) market is becoming increasingly competitive at the upper echelons, with industry leaders such as OpenAI, Google DeepMind, Anthropic, Microsoft, NVIDIA, and Meta setting the benchmark for innovation and performance. These organizations leverage substantial resources-including extensive datasets, advanced cloud infrastructure, and proprietary architectures-to maintain a significant technological advantage. Owing to which, they continue to introduce state-of-the-art transformer-based and multimodal AI systems, demonstrating ongoing improvements in contextual understanding, multilingual capabilities, and the automation of diverse business processes.
Currently, there is a pronounced shift toward the development of specialized models tailored to specific industry requirements. Notable examples include OpenAI’s GPT-4 Turbo, Anthropic’s Claude 3, and Google’s Gemini 1.5, each of which is being fine-tuned for deployment in sectors such as legal services, healthcare, and finance. Furthermore, NVIDIA’s launch of the NIM microservices platform in May 2025 exemplifies the drive to enhance operational efficiency; the platform is engineered to accelerate large language models inference for real-time enterprise applications, achieving reductions in latency and computational costs of up to 40%.
Public sector entities and research organizations are also advancing rapidly in this domain. In April 2025, the European Commission’s AI Office allocated EUR 200 million to support the development of transparent and energy-efficient AI models, aligning with the principles outlined in the EU AI Act to promote responsible AI adoption.
The large language models (LLMs) market is witnessing an expansion in accessibility and utility, driven by the proliferation of open-source initiatives and cloud-based APIs. Advances in deep learning and distributed training methodologies are enabling the creation of more efficient models, thereby accelerating growth across the large language models’ sector as an increasing number of enterprises integrate these technologies into their operations.

Recent Development and Strategic Overview:
Report Scope
|
Attribute |
Detail |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 5.9 Bn |
|
Market Forecast Value in 2035 |
USD 78.5 Bn |
|
Growth Rate (CAGR) |
29.5% |
|
Forecast Period |
2026 – 2035 |
|
Historical Data Available for |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Market Size Units |
USD Bn for Value |
|
Report Format |
Electronic (PDF) + Excel |
|
Regions and Countries Covered |
|||||
|
North America |
Europe |
Asia Pacific |
Middle East |
Africa |
South America |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Companies Covered |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Large-Language-Models-Market Segmentation and Highlights
|
Segment |
Sub-segment |
|
Large Language Models (LLM) Market, By Component |
|
|
Large Language Models (LLM) Market, By Deployment Type |
|
|
Large Language Models (LLM) Market, By Model Type |
|
|
Large Language Models (LLM) Market, By Training Approach |
|
|
Large Language Models (LLM) Market, By Enterprise Size |
|
|
Large Language Models (LLM) Market, By Function |
|
|
Large Language Models (LLM) Market, By Application |
|
|
Large Language Models (LLM) Market, By Industry Vertical |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Table of Contents
Note* - This is just tentative list of players. While providing the report, we will cover more number of players based on their revenue and share for each geography
Research Design
Our research design integrates both demand-side and supply-side analysis through a balanced combination of primary and secondary research methodologies. By utilizing both bottom-up and top-down approaches alongside rigorous data triangulation methods, we deliver robust market intelligence that supports strategic decision-making.
MarketGenics' comprehensive research design framework ensures the delivery of accurate, reliable, and actionable market intelligence. Through the integration of multiple research approaches, rigorous validation processes, and expert analysis, we provide our clients with the insights needed to make informed strategic decisions and capitalize on market opportunities.
MarketGenics leverages a dedicated industry panel of experts and a comprehensive suite of paid databases to effectively collect, consolidate, and analyze market intelligence.
Our approach has consistently proven to be reliable and effective in generating accurate market insights, identifying key industry trends, and uncovering emerging business opportunities.
Through both primary and secondary research, we capture and analyze critical company-level data such as manufacturing footprints, including technical centers, R&D facilities, sales offices, and headquarters.
Our expert panel further enhances our ability to estimate market size for specific brands based on validated field-level intelligence.
Our data mining techniques incorporate both parametric and non-parametric methods, allowing for structured data collection, sorting, processing, and cleaning.
Demand projections are derived from large-scale data sets analyzed through proprietary algorithms, culminating in robust and reliable market sizing.
Research Approach
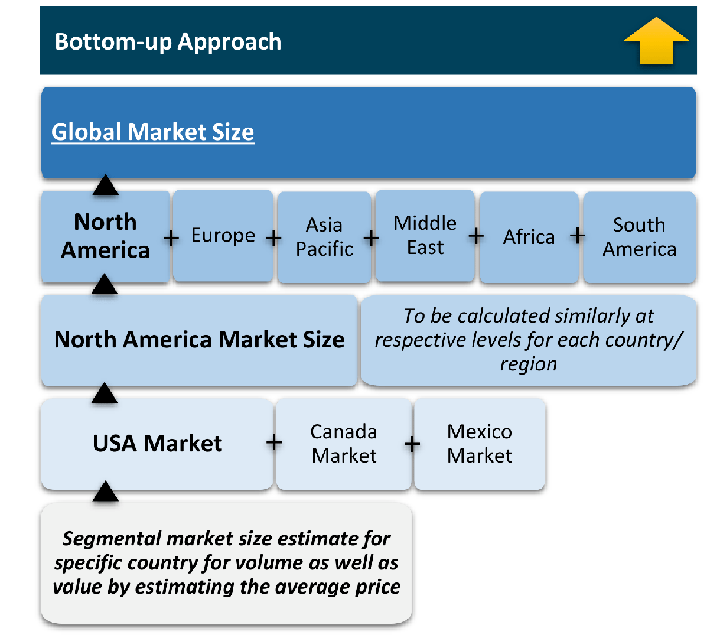
The bottom-up approach builds market estimates by starting with the smallest addressable market units and systematically aggregating them to create comprehensive market size projections.
This method begins with specific, granular data points and builds upward to create the complete market landscape.
Customer Analysis → Segmental Analysis → Geographical Analysis
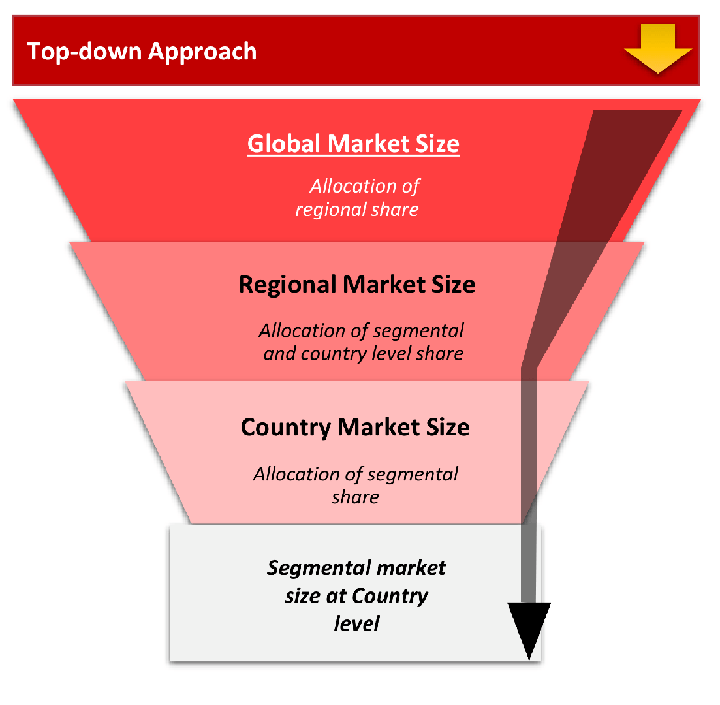
The top-down approach starts with the broadest possible market data and systematically narrows it down through a series of filters and assumptions to arrive at specific market segments or opportunities.
This method begins with the big picture and works downward to increasingly specific market slices.
TAM → SAM → SOM
Research Methods
Desk / Secondary Research
While analysing the market, we extensively study secondary sources, directories, and databases to identify and collect information useful for this technical, market-oriented, and commercial report. Secondary sources that we utilize are not only the public sources, but it is a combination of Open Source, Associations, Paid Databases, MG Repository & Knowledgebase, and others.
We also employ the model mapping approach to estimate the product level market data through the players' product portfolio
Primary Research
Primary research/ interviews is vital in analyzing the market. Most of the cases involves paid primary interviews. Primary sources include primary interviews through e-mail interactions, telephonic interviews, surveys as well as face-to-face interviews with the different stakeholders across the value chain including several industry experts.
| Type of Respondents | Number of Primaries |
|---|---|
| Tier 2/3 Suppliers | ~20 |
| Tier 1 Suppliers | ~25 |
| End-users | ~25 |
| Industry Expert/ Panel/ Consultant | ~30 |
| Total | ~100 |
MG Knowledgebase
• Repository of industry blog, newsletter and case studies
• Online platform covering detailed market reports, and company profiles
Forecasting Factors and Models
Forecasting Factors
Forecasting Models / Techniques
Multiple Regression Analysis
Time Series Analysis – Seasonal Patterns
Time Series Analysis – Trend Analysis
Expert Opinion – Expert Interviews
Multi-Scenario Development
Time Series Analysis – Moving Averages
Econometric Models
Expert Opinion – Delphi Method
Monte Carlo Simulation
Research Analysis
Our research framework is built upon the fundamental principle of validating market intelligence from both demand and supply perspectives. This dual-sided approach ensures comprehensive market understanding and reduces the risk of single-source bias.
Demand-Side Analysis: We understand end-user/application behavior, preferences, and market needs along with the penetration of the product for specific application.
Supply-Side Analysis: We estimate overall market revenue, analyze the segmental share along with industry capacity, competitive landscape, and market structure.
Validation & Evaluation
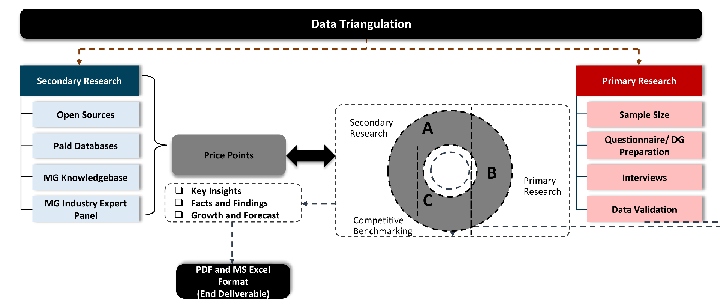
Data triangulation is a validation technique that uses multiple methods, sources, or perspectives to examine the same research question, thereby increasing the credibility and reliability of research findings. In market research, triangulation serves as a quality assurance mechanism that helps identify and minimize bias, validate assumptions, and ensure accuracy in market estimates.
Custom Market Research Services
We will customise the research for you, in case the report listed above does not meet your requirements.
Get 10% Free Customisation