Supply Chain Security Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Component (Hardware, Software and Service), Deployment Mode, Solution Type, Security Type, Organization Size, Technology, Use Case / Application, Industry Vertical and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, Africa, and South America) – Global Industry Data, Trends, and Forecasts, 2026–2035
|
Market Structure & Evolution |
|
|
Segmental Data Insights |
|
|
Demand Trends |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Strategic Development |
|
|
Future Outlook & Opportunities |
|
Supply Chain Security Market Size, Share, and Growth
The global supply chain security market is experiencing robust growth, with its estimated value of USD 2.3 billion in the year 2025 and USD 5.9 billion by the period 2035, registering a CAGR of 9.8% during the forecast period.

“Supply chain security goes beyond just protection; it is about resilience," Carrie Wibben Kaupp pointed out. She noted that with enemies progressively considering supply chains as their next battleground, companies are able-to-see-through-their-whole-enterprise and managing-their-risks-in-real-time are now the key moves that cannot be ignored.”
The supply chain security market is booming worldwide as it is influenced by several factors that are interrelated, such as technology adoption and risk management. A case in point is IBM, which in March 2025, unveiled the Supply Chain Guard platform, a tool that combines AI threat detection and blockchain traceability to give more visibility and security to supply chains that are complicated and spread worldwide.
The complexity of global logistics networks and the increasing regulatory scrutiny are leading to the intensification of the need for robust security measures. An example is the measures taken by DHL Supply Chain in June 2025 to implement advanced supply chain monitoring systems that is expected to reduce disruptions and mitigate risks in high-value shipments.
Keystandards and regulations such as ISO 28000 compliance and cybersecurity mandates are also driving organizations to upgrade their security by investing in the latest solutions. Supply chain security has been improved by higher levels of transparency, risk mitigation, and overall supply chain efficiency, which resulted from technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and the need for operational resilience, among other factors.
There are numerous interconnected opportunities in the international supply chain security market, such as blockchain-based traceability solutions, AI-powered predictive analytics, IoT-enabled asset tracking, secure logistics consulting services, and real-time risk monitoring platforms. By taking advantage of these adjacent markets, providers can not only enhance the overall resilience of the supply chain but also increase operational efficiency and create new revenue streams within the logistics and security ecosystem.

Supply Chain Security Market Dynamics and Trends
Driver: Increasing Regulatory and Compliance Requirements Driving Adoption of Advanced Supply Chain Security Solutions
- The supply chain security market volume increase is primarily highly influenced by the intensification of the regulation and compliance standard which is imposed worldwide, for example, ISO 28000, C-TPAT, and cybersecurity mandates. To prevent such situations as theft, counterfeiting, and cyber-attacks organizations have to guarantee end-to-end visibility and thus they are investing in advanced monitoring, AI-based threat detection, and blockchain-enabled traceability.
- As an example, at the end of May 2025, A.P. Moller – Maersk made a public declaration about the expansion of its next-generation IoT connectivity platform to 450 vessels, which is meant to facilitate real-time cargo tracking and thus supply-chain visibility.
- Compliance with regulations is the driver that keeps pushing corporate security departments to invest more in technologically advanced solutions. The need for real-time monitoring, transparency, and secure data handling is thus further supported.
Restraint: High Implementation and Integration Costs Limiting Widespread Adoption
- One of the reasons why advanced supply chain security systems have a difficult time being adopted is that the costs related to their execution, integration, and maintenance are quite high. To name one, a blockchain‑based traceability system combined with IoT‑enabled sensors and AI threat detection platforms entails a considerable investment not only in infrastructure and technology but also in skilled personnel.
- For instance, a report by Technavio pointed out that the use of blockchain technology in the transportation and logistics industry is going to increase significantly from 2024 to 2028; however, it also emphasized that the high implementation cost is still the major obstacle.
- These expenses may cause the implementation of new solutions to be postponed, thus small and medium enterprises or regional logistics providers are affected in particular, and the rate of adoption is slowed down even though the security is enhanced.
Opportunity: Growing Demand in Emerging and Regional Markets
- Supply chain security vendors are expected to find huge growth potentials in the developing markets of Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America. The triple phenomena of e-commerce, regional manufacturing, and cross-border trade are raising the need for logistics solutions that are not only secure and compliant but also technologically advanced.
- The modernization and standardization to global norms of regional logistics and manufacturing industries is expected to give supply chain security providers the opportunities to broaden their customer base and income sources by delivering scalable, budget-friendly, and compliant solutions.
Key Trend: Integration of Smart, IoT, and AI‑Enabled Supply Chain Security Systems
- One of the major trends in the supply chain security market is the move towards connected, AI‑enabled, and IoT‑integrated security systems. These kinds of technologies allow for real‑time tracking, predictive risk analysis, and in some cases, automated alerts which help in preventing theft, tampering, and operational disruptions.
- In order to illustrate, as part of the network upgrade, Maersk is installing private LTE/IoT connectivity on hundreds of vessels, thus, thousands of devices will be able to monitor cargo and asset conditions in real‑time.
- Their connectivity and intelligence features make supply chain security systems more reliable in terms of operational risk and compliance while at the same time, they are less prone to human error. The pace of such technology adoption is getting faster as companies are willing to comply with the changing global safety standards, secure their assets, and increase operational efficiency.
Supply Chain Security Market Analysis and Segmental Data

Large Enterprises Maintain Dominance in Global Supply Chain Security Market amid Growing Technological and Regulatory Demands
- Large enterprises have the largest share of the global supply chain security market and will most likely continue to dominate the market due to their complex, multi-level supply networks with higher exposure to operational and cyber risks. One of their major advantages is that they can invest in advanced technologies such as IoT-enabled tracking, AI-based threat detection, and blockchain for end-to-end transparency.
- By way of illustration, Maersk’s implementation of its next-generation IoT connectivity platform across 450 vessels in 2025 is a move that enables real-time cargo monitoring and predictive risk analytics, thus, it not only increases operational efficiency but also facilitates regulatory compliance. Conforming to stricter worldwide standards such as ISO 28000 and C‑TPAT, large enterprises are turning to the automated, intelligent security solutions as a means of guaranteeing supply-chain resilience.
- The interplay of factors such as regulatory pressure, technological advancement, and operational scale is still working to the advantage of large enterprises that are consolidating their leading position in the market.
Strengthened Supply Chain Security Market Elevating North American Market amid Technological Innovation and Regulatory Enforcement
- North America is at the forefront of the worldwide supply chain security market which can be attributed to its highly sophisticated digital infrastructure, strict enforcement of regulations, and the need for real-time monitoring of intricate logistics networks. The region held the largest share of the market, in 2024 with the support of rigorous compliance requirements and the extensive implementation of sophisticated security measures.
- For instance, Maersk has rolled out its next-generation IoT connectivity platform on hundreds of vessels in North America in 2025, thereby enabling real-time cargo monitoring, predictive risk analytics, and enhanced supply-chain resilience. The supply chain security report of 2023 by the Department of Homeland Security is only one example of many government initiatives that clearly demonstrate the region’s emphasis on regulatory oversight and risk mitigation.
- Meanwhile, logistics and technology providers are implementing AI-powered threat analytics and blockchain-based traceability to improve operational efficiency and meet the requirements of the changing regulations. All these factors make North America the top market for supply chain security solutions worldwide.
Supply-Chain-Security-Market Ecosystem
The global supply chain security market has become moderately consolidated over time, with only a handful of major players leading the way. These include IBM Corporation, Cisco Systems, Inc., Fortinet, Inc., Check Point Software Technologies Ltd., Palo Alto Networks, Inc., and Accenture plc, which by incorporating advanced technologies - AI, blockchain, and IoT - into their offerings, have been able to dominate the market. These large-scale enterprises combine their profound cybersecurity knowledge and worldwide network to grab a significant portion of the market.
These companies concentrate on small markets or highly specialized areas, for instance, Check Point utilizes threat intelligence platforms for supply-chain vendor risk, Palo Alto Networks provides integrated cloud-based supply-chain governance tools, Accenture offers consulting services on digital-supply-chain resilience, and Cisco delivers IoT sensor security for logistics networks.
Besides them, government authorities and academic institutions are energizing the innovation wheel. One illustration is IBM's unveiling in May 2024 of its "Supply Chain Resiliency" module in its Sterling® Order Management suite, equipped with AI analytics and real-time pattern recognition, thus, enabling users to detect disruptions and improve on-time-in-full (OTIF) rates. As a countermove, significant players are turning to product diversification and portfolio expansion as their main strategies.
Fortinet, on the other hand, in April 2025, disseminated its FortiAI innovations throughout its Security Fabric platform to not only facilitate supply-chain threat detection but also enable the automation of network operations, thus increasing operational efficiency.

Recent Development and Strategic Overview:
- In April 2025, Fortinet, Inc. enhanced the integration of its FortiAI-Protect features with Security Fabric platform by introducing AI-driven threat detection, automated alert triage, and root-cause tracing to empower supply-chain security and decrease the response time.
- In March 2025, Cisco Systems, Inc. and NVIDIA Corporation announced the Secure AI Factory architecture that redefines security at every layer of industrial IoT and AI infrastructure. As a result, real-time monitoring of logistics nodes and networked assets is possible, thus strengthening supply-chain resilience.
Report Scope
|
Attribute |
Detail |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 2.3 Bn |
|
Market Forecast Value in 2035 |
USD 5.9 Bn |
|
Growth Rate (CAGR) |
9.8% |
|
Forecast Period |
2026 – 2035 |
|
Historical Data Available for |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Market Size Units |
USD Bn for Value |
|
Report Format |
Electronic (PDF) + Excel |
|
Regions and Countries Covered |
|||||
|
North America |
Europe |
Asia Pacific |
Middle East |
Africa |
South America |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Companies Covered |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supply-Chain-Security-Market Segmentation and Highlights
|
Segment |
Sub-segment |
|
Supply Chain Security Market, By Component |
|
|
Supply Chain Security Market, By Deployment Mode |
|
|
Supply Chain Security Market, By Solution Type |
|
|
Supply Chain Security Market, By Security Type |
|
|
Supply Chain Security Market, By Organization Size |
|
|
Supply Chain Security Market, By Technology |
|
|
Supply Chain Security Market, By Industry Vertical |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Table of Contents
- 1. Research Methodology and Assumptions
- 1.1. Definitions
- 1.2. Research Design and Approach
- 1.3. Data Collection Methods
- 1.4. Base Estimates and Calculations
- 1.5. Forecasting Models
- 1.5.1. Key Forecast Factors & Impact Analysis
- 1.6. Secondary Research
- 1.6.1. Open Sources
- 1.6.2. Paid Databases
- 1.6.3. Associations
- 1.7. Primary Research
- 1.7.1. Primary Sources
- 1.7.2. Primary Interviews with Stakeholders across Ecosystem
- 2. Executive Summary
- 2.1. Global Supply Chain Security Market Outlook
- 2.1.1. Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 2.1.2. Compounded Annual Growth Rate Analysis
- 2.1.3. Growth Opportunity Analysis
- 2.1.4. Segmental Share Analysis
- 2.1.5. Geographical Share Analysis
- 2.2. Market Analysis and Facts
- 2.3. Supply-Demand Analysis
- 2.4. Competitive Benchmarking
- 2.5. Go-to- Market Strategy
- 2.5.1. Customer/ End-use Industry Assessment
- 2.5.2. Growth Opportunity Data, 2026-2035
- 2.5.2.1. Regional Data
- 2.5.2.2. Country Data
- 2.5.2.3. Segmental Data
- 2.5.3. Identification of Potential Market Spaces
- 2.5.4. GAP Analysis
- 2.5.5. Potential Attractive Price Points
- 2.5.6. Prevailing Market Risks & Challenges
- 2.5.7. Preferred Sales & Marketing Strategies
- 2.5.8. Key Recommendations and Analysis
- 2.5.9. A Way Forward
- 2.1. Global Supply Chain Security Market Outlook
- 3. Industry Data and Premium Insights
- 3.1. Global Information Technology & Media Ecosystem Overview, 2025
- 3.1.1. Information Technology & Media Ecosystem Analysis
- 3.1.2. Key Trends for Information Technology & Media Industry
- 3.1.3. Regional Distribution for Information Technology & Media Industry
- 3.2. Supplier Customer Data
- 3.3. Technology Roadmap and Developments
- 3.1. Global Information Technology & Media Ecosystem Overview, 2025
- 4. Market Overview
- 4.1. Market Dynamics
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.1.1.1. Rising demand for end-to-end visibility and real-time monitoring across global supply chains
- 4.1.1.2. Growing adoption of IoT-enabled sensors, blockchain, and AI/ML-driven analytics for threat detection and risk management
- 4.1.1.3. Increasing regulatory requirements and standards for product authenticity, traceability, and cybersecurity in supply chains
- 4.1.2. Restraints
- 4.1.2.1. High implementation and operational costs of advanced supply chain security solutions
- 4.1.2.2. Complexity in integrating security technologies with legacy logistics systems and multi-tier supplier
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.2. Key Trend Analysis
- 4.3. Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1. Key Regulations, Norms, and Subsidies, by Key Countries
- 4.3.2. Tariffs and Standards
- 4.3.3. Impact Analysis of Regulations on the Market
- 4.4. Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4.1. Risk Assessment/ Supplier Verification Suppliers
- 4.4.2. System Integrators/ Technology Providers
- 4.4.3. Supply Chain Security Providers
- 4.4.4. End Users
- 4.5. Cost Structure Analysis
- 4.5.1. Parameter’s Share for Cost Associated
- 4.5.2. COGP vs COGS
- 4.5.3. Profit Margin Analysis
- 4.6. Pricing Analysis
- 4.6.1. Regional Pricing Analysis
- 4.6.2. Segmental Pricing Trends
- 4.6.3. Factors Influencing Pricing
- 4.7. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8. PESTEL Analysis
- 4.9. Global Supply Chain Security Market Demand
- 4.9.1. Historical Market Size –Value (US$ Bn), 2020-2024
- 4.9.2. Current and Future Market Size –Value (US$ Bn), 2026–2035
- 4.9.2.1. Y-o-Y Growth Trends
- 4.9.2.2. Absolute $ Opportunity Assessment
- 4.1. Market Dynamics
- 5. Competition Landscape
- 5.1. Competition structure
- 5.1.1. Fragmented v/s consolidated
- 5.2. Company Share Analysis, 2025
- 5.2.1. Global Company Market Share
- 5.2.2. By Region
- 5.2.2.1. North America
- 5.2.2.2. Europe
- 5.2.2.3. Asia Pacific
- 5.2.2.4. Middle East
- 5.2.2.5. Africa
- 5.2.2.6. South America
- 5.3. Product Comparison Matrix
- 5.3.1. Specifications
- 5.3.2. Market Positioning
- 5.3.3. Pricing
- 5.1. Competition structure
- 6. Global Supply Chain Security Market Analysis, by Component
- 6.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 6.2. Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Component, 2021-2035
- 6.2.1. Hardware
- 6.2.1.1. RFID Tags & Readers
- 6.2.1.2. GPS Trackers & IoT Sensors
- 6.2.1.3. Biometric Access Devices
- 6.2.1.4. Security Cameras & Surveillance Systems
- 6.2.1.5. Tamper-evident Packaging Devices
- 6.2.1.6. Others
- 6.2.2. Software
- 6.2.2.1. Supply Chain Risk Management Software
- 6.2.2.2. Blockchain-based Provenance Platforms
- 6.2.2.3. Data Analytics & AI-driven Threat Detection Tools
- 6.2.2.4. Inventory & Asset Visibility Software
- 6.2.2.5. Encryption & Identity Management Software
- 6.2.2.6. Others
- 6.2.3. Service
- 6.2.3.1. Professional Services
- 6.2.3.2. Managed Security Services (MSS)
- 6.2.3.3. Training & Support Services
- 6.2.3.4. Integration & Maintenance Services
- 6.2.3.5. Others
- 6.2.1. Hardware
- 7. Global Supply Chain Security Market Analysis, by Deployment Mode
- 7.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 7.2. Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Deployment Mode, 2021-2035
- 7.2.1. Cloud-Based
- 7.2.2. On-Premises
- 7.2.3. Hybrid
- 8. Global Supply Chain Security Market Analysis, by Solution Type
- 8.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 8.2. Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Solution Type, 2021-2035
- 8.2.1. Supply Chain Risk Management Platforms
- 8.2.2. Asset Tracking & Visibility Solutions
- 8.2.3. Identity & Access Management for Suppliers
- 8.2.4. Threat Detection & Anomaly Detection
- 8.2.5. Tamper-evident Packaging & IoT-enabled Seals
- 8.2.6. Blockchain-based Provenance Solutions
- 8.2.7. Secure Firmware & Software Signing Tools
- 8.2.8. Others
- 9. Global Supply Chain Security Market Analysis, by Security Type
- 9.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 9.2. Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Security Type, 2021-2035
- 9.2.1. Cybersecurity for Supply Chain (software/firmware risks)
- 9.2.2. Physical Security (cargo, warehouse, transport)
- 9.2.3. Operational Security (process, people, policies)
- 9.2.4. Compliance & Regulatory Security
- 9.2.5. Others
- 10. Global Supply Chain Security Market Analysis, by Organization Size
- 10.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 10.2. Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Organization Size, 2021-2035
- 10.2.1. Large Enterprises
- 10.2.2. Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- 11. Global Supply Chain Security Market Analysis, by Technology
- 11.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 11.2. Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Technology, 2021-2035
- 11.2.1. IoT & Telemetry (GPS, RFID, sensors)
- 11.2.2. AI/ML Analytics & Anomaly Detection
- 11.2.3. Blockchain & Distributed Ledger Technology
- 11.2.4. Secure Enclaves / Trusted Execution Environments
- 11.2.5. Encryption & Key Management
- 11.2.6. Others
- 12. Global Supply Chain Security Market Analysis, by Use Case / Application
- 12.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 12.2. Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Use Case / Application, 2021-2035
- 12.2.1. Counterfeit Prevention & Anti-tampering
- 12.2.2. Cargo Theft Prevention & Recovery
- 12.2.3. Supplier Risk Assessment & Monitoring
- 12.2.4. Cold Chain Integrity Monitoring
- 12.2.5. Regulatory Compliance & Audit Trail
- 12.2.6. Others
- 13. Global Supply Chain Security Market Analysis, by Industry Vertical
- 13.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 13.2. Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Industry Vertical, 2021-2035
- 13.2.1. Automotive
- 13.2.2. Aerospace & Defense
- 13.2.3. Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
- 13.2.4. Retail & Consumer Goods
- 13.2.5. Electronics & High-tech
- 13.2.6. Food & Beverage
- 13.2.7. Energy & Utilities
- 13.2.8. Logistics & Transportation
- 13.2.9. Others
- 14. Global Supply Chain Security Market Analysis and Forecasts, by Region
- 14.1. Key Findings
- 14.2. Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Region, 2021-2035
- 14.2.1. North America
- 14.2.2. Europe
- 14.2.3. Asia Pacific
- 14.2.4. Middle East
- 14.2.5. Africa
- 14.2.6. South America
- 15. North America Supply Chain Security Market Analysis
- 15.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 15.2. Regional Snapshot
- 15.3. North America Supply Chain Security Market Size Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 15.3.1. Component
- 15.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 15.3.3. Solution Type
- 15.3.4. Security Type
- 15.3.5. Organization Size
- 15.3.6. Technology
- 15.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 15.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 15.3.9. Country
- 15.3.9.1. USA
- 15.3.9.2. Canada
- 15.3.9.3. Mexico
- 15.4. USA Supply Chain Security Market
- 15.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.4.2. Component
- 15.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 15.4.4. Solution Type
- 15.4.5. Security Type
- 15.4.6. Organization Size
- 15.4.7. Technology
- 15.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 15.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 15.5. Canada Supply Chain Security Market
- 15.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.5.2. Component
- 15.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 15.5.4. Solution Type
- 15.5.5. Security Type
- 15.5.6. Organization Size
- 15.5.7. Technology
- 15.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 15.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 15.6. Mexico Supply Chain Security Market
- 15.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 15.6.2. Component
- 15.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 15.6.4. Solution Type
- 15.6.5. Security Type
- 15.6.6. Organization Size
- 15.6.7. Technology
- 15.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 15.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 16. Europe Supply Chain Security Market Analysis
- 16.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 16.2. Regional Snapshot
- 16.3. Europe Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 16.3.1. Component
- 16.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 16.3.3. Solution Type
- 16.3.4. Security Type
- 16.3.5. Organization Size
- 16.3.6. Technology
- 16.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 16.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 16.3.9. Country
- 16.3.9.1. Germany
- 16.3.9.2. United Kingdom
- 16.3.9.3. France
- 16.3.9.4. Italy
- 16.3.9.5. Spain
- 16.3.9.6. Netherlands
- 16.3.9.7. Nordic Countries
- 16.3.9.8. Poland
- 16.3.9.9. Russia & CIS
- 16.3.9.10. Rest of Europe
- 16.4. Germany Supply Chain Security Market
- 16.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.4.2. Component
- 16.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.4.4. Solution Type
- 16.4.5. Security Type
- 16.4.6. Organization Size
- 16.4.7. Technology
- 16.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.5. United Kingdom Supply Chain Security Market
- 16.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.5.2. Component
- 16.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.5.4. Solution Type
- 16.5.5. Security Type
- 16.5.6. Organization Size
- 16.5.7. Technology
- 16.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.6. France Supply Chain Security Market
- 16.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.6.2. Component
- 16.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.6.4. Solution Type
- 16.6.5. Security Type
- 16.6.6. Organization Size
- 16.6.7. Technology
- 16.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.7. Italy Supply Chain Security Market
- 16.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.7.2. Component
- 16.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.7.4. Solution Type
- 16.7.5. Security Type
- 16.7.6. Organization Size
- 16.7.7. Technology
- 16.7.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.7.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.8. Spain Supply Chain Security Market
- 16.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.8.2. Component
- 16.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.8.4. Solution Type
- 16.8.5. Security Type
- 16.8.6. Organization Size
- 16.8.7. Technology
- 16.8.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.8.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.9. Netherlands Supply Chain Security Market
- 16.9.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.9.2. Component
- 16.9.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.9.4. Solution Type
- 16.9.5. Security Type
- 16.9.6. Organization Size
- 16.9.7. Technology
- 16.9.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.9.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.10. Nordic Countries Supply Chain Security Market
- 16.10.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.10.2. Component
- 16.10.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.10.4. Solution Type
- 16.10.5. Security Type
- 16.10.6. Organization Size
- 16.10.7. Technology
- 16.10.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.10.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.11. Poland Supply Chain Security Market
- 16.11.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.11.2. Component
- 16.11.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.11.4. Solution Type
- 16.11.5. Security Type
- 16.11.6. Organization Size
- 16.11.7. Technology
- 16.11.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.11.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.12. Russia & CIS Supply Chain Security Market
- 16.12.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.12.2. Component
- 16.12.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.12.4. Solution Type
- 16.12.5. Security Type
- 16.12.6. Organization Size
- 16.12.7. Technology
- 16.12.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.12.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.13. Rest of Europe Supply Chain Security Market
- 16.13.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.13.2. Component
- 16.13.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.13.4. Solution Type
- 16.13.5. Security Type
- 16.13.6. Organization Size
- 16.13.7. Technology
- 16.13.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.13.9. Industry Vertical
- 17. Asia Pacific Supply Chain Security Market Analysis
- 17.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 17.2. Regional Snapshot
- 17.3. Asia Pacific Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 17.3.1. Component
- 17.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 17.3.3. Solution Type
- 17.3.4. Security Type
- 17.3.5. Organization Size
- 17.3.6. Technology
- 17.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 17.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 17.3.9. Country
- 17.3.9.1. China
- 17.3.9.2. India
- 17.3.9.3. Japan
- 17.3.9.4. South Korea
- 17.3.9.5. Australia and New Zealand
- 17.3.9.6. Indonesia
- 17.3.9.7. Malaysia
- 17.3.9.8. Thailand
- 17.3.9.9. Vietnam
- 17.3.9.10. Rest of Asia Pacific
- 17.4. China Supply Chain Security Market
- 17.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.4.2. Component
- 17.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.4.4. Solution Type
- 17.4.5. Security Type
- 17.4.6. Organization Size
- 17.4.7. Technology
- 17.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.5. India Supply Chain Security Market
- 17.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.5.2. Component
- 17.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.5.4. Solution Type
- 17.5.5. Security Type
- 17.5.6. Organization Size
- 17.5.7. Technology
- 17.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.6. Japan Supply Chain Security Market
- 17.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.6.2. Component
- 17.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.6.4. Solution Type
- 17.6.5. Security Type
- 17.6.6. Organization Size
- 17.6.7. Technology
- 17.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.7. South Korea Supply Chain Security Market
- 17.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.7.2. Component
- 17.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.7.4. Solution Type
- 17.7.5. Security Type
- 17.7.6. Organization Size
- 17.7.7. Technology
- 17.7.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.7.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.8. Australia and New Zealand Supply Chain Security Market
- 17.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.8.2. Component
- 17.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.8.4. Solution Type
- 17.8.5. Security Type
- 17.8.6. Organization Size
- 17.8.7. Technology
- 17.8.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.8.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.9. Indonesia Supply Chain Security Market
- 17.9.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.9.2. Component
- 17.9.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.9.4. Solution Type
- 17.9.5. Security Type
- 17.9.6. Organization Size
- 17.9.7. Technology
- 17.9.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.9.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.10. Malaysia Supply Chain Security Market
- 17.10.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.10.2. Component
- 17.10.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.10.4. Solution Type
- 17.10.5. Security Type
- 17.10.6. Organization Size
- 17.10.7. Technology
- 17.10.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.10.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.11. Thailand Supply Chain Security Market
- 17.11.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.11.2. Component
- 17.11.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.11.4. Solution Type
- 17.11.5. Security Type
- 17.11.6. Organization Size
- 17.11.7. Technology
- 17.11.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.11.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.12. Vietnam Supply Chain Security Market
- 17.12.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.12.2. Component
- 17.12.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.12.4. Solution Type
- 17.12.5. Security Type
- 17.12.6. Organization Size
- 17.12.7. Technology
- 17.12.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.12.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.13. Rest of Asia Pacific Supply Chain Security Market
- 17.13.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.13.2. Component
- 17.13.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.13.4. Solution Type
- 17.13.5. Security Type
- 17.13.6. Organization Size
- 17.13.7. Technology
- 17.13.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.13.9. Industry Vertical
- 18. Middle East Supply Chain Security Market Analysis
- 18.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 18.2. Regional Snapshot
- 18.3. Middle East Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 18.3.1. Component
- 18.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 18.3.3. Solution Type
- 18.3.4. Security Type
- 18.3.5. Organization Size
- 18.3.6. Technology
- 18.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 18.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 18.3.9. Country
- 18.3.9.1. Turkey
- 18.3.9.2. UAE
- 18.3.9.3. Saudi Arabia
- 18.3.9.4. Israel
- 18.3.9.5. Rest of Middle East
- 18.4. Turkey Supply Chain Security Market
- 18.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.4.2. Component
- 18.4.3. Authentication Method
- 18.4.4. Technology
- 18.4.5. Deployment Type
- 18.4.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.4.7. Application
- 18.4.8. Industry Vertical
- 18.5. UAE Supply Chain Security Market
- 18.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.5.2. Component
- 18.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.5.4. Solution Type
- 18.5.5. Security Type
- 18.5.6. Organization Size
- 18.5.7. Technology
- 18.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 18.6. Saudi Arabia Supply Chain Security Market
- 18.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.6.2. Component
- 18.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.6.4. Solution Type
- 18.6.5. Security Type
- 18.6.6. Organization Size
- 18.6.7. Technology
- 18.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 18.7. Israel Supply Chain Security Market
- 18.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.7.2. Component
- 18.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.7.4. Solution Type
- 18.7.5. Security Type
- 18.7.6. Organization Size
- 18.7.7. Technology
- 18.7.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.7.9. Industry Vertical
- 18.8. Rest of Middle East Supply Chain Security Market
- 18.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.8.2. Component
- 18.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.8.4. Solution Type
- 18.8.5. Security Type
- 18.8.6. Organization Size
- 18.8.7. Technology
- 18.8.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.8.9. Industry Vertical
- 19. Africa Supply Chain Security Market Analysis
- 19.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 19.2. Regional Snapshot
- 19.3. Africa Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 19.3.1. Component
- 19.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 19.3.3. Solution Type
- 19.3.4. Security Type
- 19.3.5. Organization Size
- 19.3.6. Technology
- 19.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 19.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 19.3.9. Country
- 19.3.9.1. South Africa
- 19.3.9.2. Egypt
- 19.3.9.3. Nigeria
- 19.3.9.4. Algeria
- 19.3.9.5. Rest of Africa
- 19.4. South Africa Supply Chain Security Market
- 19.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.4.2. Component
- 19.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.4.4. Solution Type
- 19.4.5. Security Type
- 19.4.6. Organization Size
- 19.4.7. Technology
- 19.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 19.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 19.5. Egypt Supply Chain Security Market
- 19.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.5.2. Component
- 19.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.5.4. Solution Type
- 19.5.5. Security Type
- 19.5.6. Organization Size
- 19.5.7. Technology
- 19.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 19.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 19.6. Nigeria Supply Chain Security Market
- 19.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.6.2. Component
- 19.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.6.4. Solution Type
- 19.6.5. Security Type
- 19.6.6. Organization Size
- 19.6.7. Technology
- 19.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 19.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 19.7. Algeria Supply Chain Security Market
- 19.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.7.2. Component
- 19.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.7.4. Solution Type
- 19.7.5. Security Type
- 19.7.6. Organization Size
- 19.7.7. Technology
- 19.7.8. Use Case / Application
- 19.7.9. Industry Vertical
- 19.8. Rest of Africa Supply Chain Security Market
- 19.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.8.2. Component
- 19.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.8.4. Solution Type
- 19.8.5. Security Type
- 19.8.6. Organization Size
- 19.8.7. Technology
- 19.8.8. Use Case / Application
- 19.8.9. Industry Vertical
- 20. South America Supply Chain Security Market Analysis
- 20.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 20.2. Regional Snapshot
- 20.3. South America Supply Chain Security Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 20.3.1. Component
- 20.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 20.3.3. Solution Type
- 20.3.4. Security Type
- 20.3.5. Organization Size
- 20.3.6. Technology
- 20.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 20.3.8. Industry Vertical
- 20.3.9. Country
- 20.3.9.1. Brazil
- 20.3.9.2. Argentina
- 20.3.9.3. Rest of South America
- 20.4. Brazil Supply Chain Security Market
- 20.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.4.2. Component
- 20.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.4.4. Solution Type
- 20.4.5. Security Type
- 20.4.6. Organization Size
- 20.4.7. Technology
- 20.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 20.4.9. Industry Vertical
- 20.5. Argentina Supply Chain Security Market
- 20.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.5.2. Component
- 20.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.5.4. Solution Type
- 20.5.5. Security Type
- 20.5.6. Organization Size
- 20.5.7. Technology
- 20.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 20.5.9. Industry Vertical
- 20.6. Rest of South America Supply Chain Security Market
- 20.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.6.2. Component
- 20.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.6.4. Solution Type
- 20.6.5. Security Type
- 20.6.6. Organization Size
- 20.6.7. Technology
- 20.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 20.6.9. Industry Vertical
- 21. Key Players/ Company Profile
- 21.1. Accenture plc
- 21.1.1. Company Details/ Overview
- 21.1.2. Company Financials
- 21.1.3. Key Customers and Competitors
- 21.1.4. Business/ Industry Portfolio
- 21.1.5. Product Portfolio/ Specification Details
- 21.1.6. Pricing Data
- 21.1.7. Strategic Overview
- 21.1.8. Recent Developments
- 21.2. BAE Systems plc
- 21.3. Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- 21.4. Cisco Systems, Inc.
- 21.5. CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc.
- 21.6. Deloitte LLP
- 21.7. Ernst & Young Global Limited
- 21.8. Fortinet, Inc.
- 21.9. Honeywell International Inc.
- 21.10. International Business Machines Corporation (IBM)
- 21.11. KPMG International Cooperative
- 21.12. Leidos Holdings, Inc.
- 21.13. Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 21.14. Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- 21.15. Rapid7, Inc.
- 21.16. Raytheon Technologies Corporation
- 21.17. Robert Bosch GmbH
- 21.18. Siemens AG
- 21.19. Thales Group
- 21.20. Verizon Communications Inc.
- 21.21. Others Key Players
- 21.1. Accenture plc
Note* - This is just tentative list of players. While providing the report, we will cover more number of players based on their revenue and share for each geography
Research Design
Our research design integrates both demand-side and supply-side analysis through a balanced combination of primary and secondary research methodologies. By utilizing both bottom-up and top-down approaches alongside rigorous data triangulation methods, we deliver robust market intelligence that supports strategic decision-making.
MarketGenics' comprehensive research design framework ensures the delivery of accurate, reliable, and actionable market intelligence. Through the integration of multiple research approaches, rigorous validation processes, and expert analysis, we provide our clients with the insights needed to make informed strategic decisions and capitalize on market opportunities.
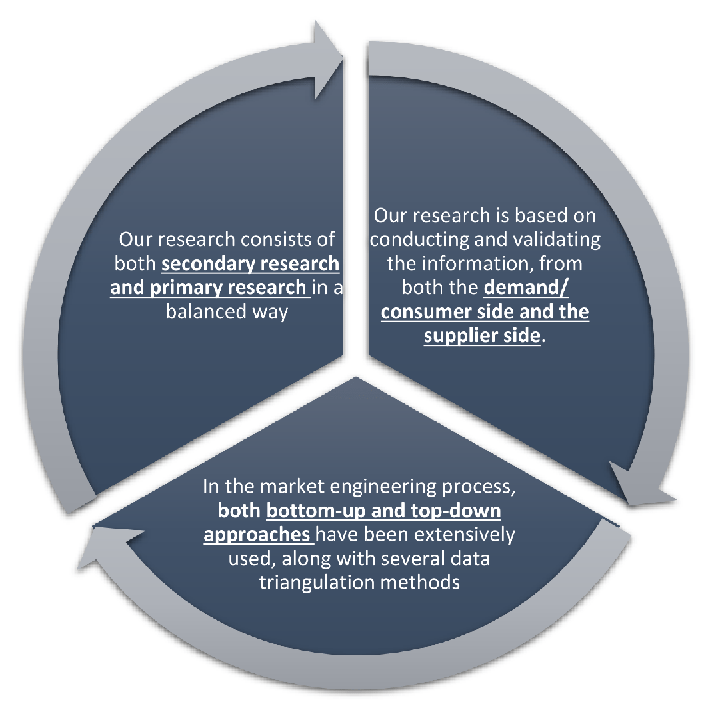
MarketGenics leverages a dedicated industry panel of experts and a comprehensive suite of paid databases to effectively collect, consolidate, and analyze market intelligence.
Our approach has consistently proven to be reliable and effective in generating accurate market insights, identifying key industry trends, and uncovering emerging business opportunities.
Through both primary and secondary research, we capture and analyze critical company-level data such as manufacturing footprints, including technical centers, R&D facilities, sales offices, and headquarters.
Our expert panel further enhances our ability to estimate market size for specific brands based on validated field-level intelligence.
Our data mining techniques incorporate both parametric and non-parametric methods, allowing for structured data collection, sorting, processing, and cleaning.
Demand projections are derived from large-scale data sets analyzed through proprietary algorithms, culminating in robust and reliable market sizing.
Research Approach
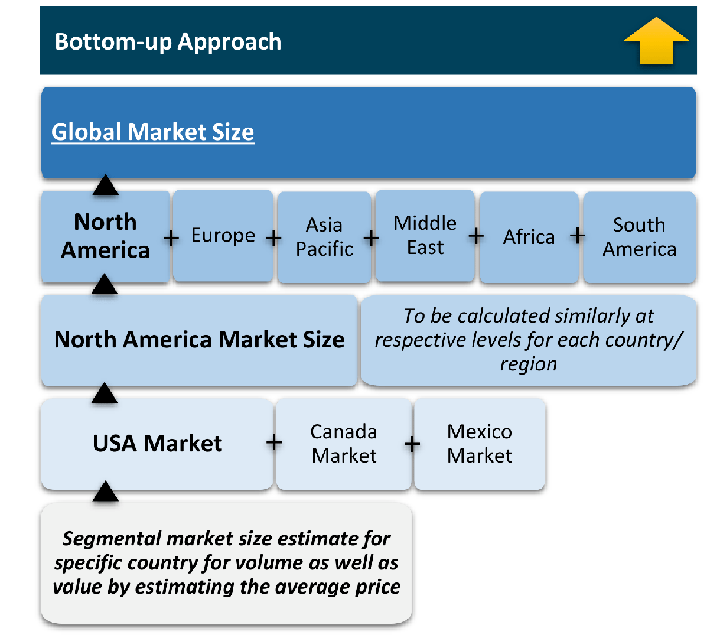
The bottom-up approach builds market estimates by starting with the smallest addressable market units and systematically aggregating them to create comprehensive market size projections.
This method begins with specific, granular data points and builds upward to create the complete market landscape.
Customer Analysis → Segmental Analysis → Geographical Analysis
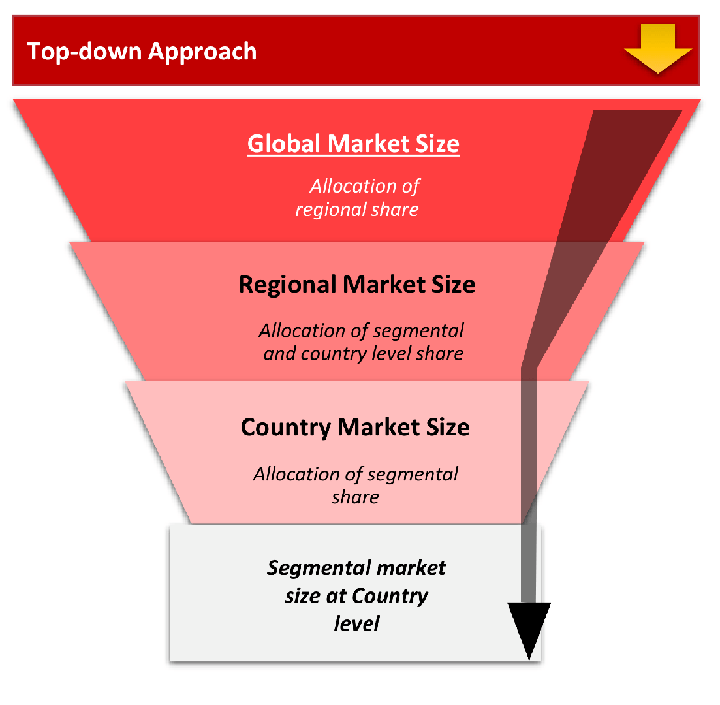
The top-down approach starts with the broadest possible market data and systematically narrows it down through a series of filters and assumptions to arrive at specific market segments or opportunities.
This method begins with the big picture and works downward to increasingly specific market slices.
TAM → SAM → SOM
Research Methods
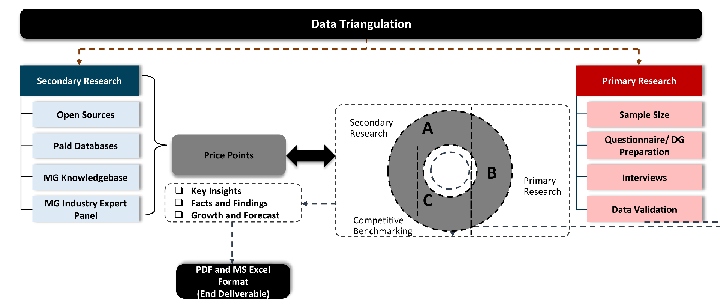
Desk / Secondary Research
While analysing the market, we extensively study secondary sources, directories, and databases to identify and collect information useful for this technical, market-oriented, and commercial report. Secondary sources that we utilize are not only the public sources, but it is a combination of Open Source, Associations, Paid Databases, MG Repository & Knowledgebase, and others.
- Company websites, annual reports, financial reports, broker reports, and investor presentations
- National government documents, statistical databases and reports
- News articles, press releases and web-casts specific to the companies operating in the market, Magazines, reports, and others
- We gather information from commercial data sources for deriving company specific data such as segmental revenue, share for geography, product revenue, and others
- Internal and external proprietary databases (industry-specific), relevant patent, and regulatory databases
- Governing Bodies, Government Organizations
- Relevant Authorities, Country-specific Associations for Industries
We also employ the model mapping approach to estimate the product level market data through the players' product portfolio
Primary Research
Primary research/ interviews is vital in analyzing the market. Most of the cases involves paid primary interviews. Primary sources include primary interviews through e-mail interactions, telephonic interviews, surveys as well as face-to-face interviews with the different stakeholders across the value chain including several industry experts.
| Type of Respondents | Number of Primaries |
|---|---|
| Tier 2/3 Suppliers | ~20 |
| Tier 1 Suppliers | ~25 |
| End-users | ~25 |
| Industry Expert/ Panel/ Consultant | ~30 |
| Total | ~100 |
MG Knowledgebase
• Repository of industry blog, newsletter and case studies
• Online platform covering detailed market reports, and company profiles
Forecasting Factors and Models
Forecasting Factors
- Historical Trends – Past market patterns, cycles, and major events that shaped how markets behave over time. Understanding past trends helps predict future behavior.
- Industry Factors – Specific characteristics of the industry like structure, regulations, and innovation cycles that affect market dynamics.
- Macroeconomic Factors – Economic conditions like GDP growth, inflation, and employment rates that affect how much money people have to spend.
- Demographic Factors – Population characteristics like age, income, and location that determine who can buy your product.
- Technology Factors – How quickly people adopt new technology and how much technology infrastructure exists.
- Regulatory Factors – Government rules, laws, and policies that can help or restrict market growth.
- Competitive Factors – Analyzing competition structure such as degree of competition and bargaining power of buyers and suppliers.
Forecasting Models / Techniques
Multiple Regression Analysis
- Identify and quantify factors that drive market changes
- Statistical modeling to establish relationships between market drivers and outcomes
Time Series Analysis – Seasonal Patterns
- Understand regular cyclical patterns in market demand
- Advanced statistical techniques to separate trend, seasonal, and irregular components
Time Series Analysis – Trend Analysis
- Identify underlying market growth patterns and momentum
- Statistical analysis of historical data to project future trends
Expert Opinion – Expert Interviews
- Gather deep industry insights and contextual understanding
- In-depth interviews with key industry stakeholders
Multi-Scenario Development
- Prepare for uncertainty by modeling different possible futures
- Creating optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely scenarios
Time Series Analysis – Moving Averages
- Sophisticated forecasting for complex time series data
- Auto-regressive integrated moving average models with seasonal components
Econometric Models
- Apply economic theory to market forecasting
- Sophisticated economic models that account for market interactions
Expert Opinion – Delphi Method
- Harness collective wisdom of industry experts
- Structured, multi-round expert consultation process
Monte Carlo Simulation
- Quantify uncertainty and probability distributions
- Thousands of simulations with varying input parameters
Research Analysis
Our research framework is built upon the fundamental principle of validating market intelligence from both demand and supply perspectives. This dual-sided approach ensures comprehensive market understanding and reduces the risk of single-source bias.
Demand-Side Analysis: We understand end-user/application behavior, preferences, and market needs along with the penetration of the product for specific application.
Supply-Side Analysis: We estimate overall market revenue, analyze the segmental share along with industry capacity, competitive landscape, and market structure.
Validation & Evaluation
Data triangulation is a validation technique that uses multiple methods, sources, or perspectives to examine the same research question, thereby increasing the credibility and reliability of research findings. In market research, triangulation serves as a quality assurance mechanism that helps identify and minimize bias, validate assumptions, and ensure accuracy in market estimates.
- Data Source Triangulation – Using multiple data sources to examine the same phenomenon
- Methodological Triangulation – Using multiple research methods to study the same research question
- Investigator Triangulation – Using multiple researchers or analysts to examine the same data
- Theoretical Triangulation – Using multiple theoretical perspectives to interpret the same data
Custom Market Research Services
We will customise the research for you, in case the report listed above does not meet your requirements.
Get 10% Free Customisation