- The global zero trust architecture market is valued at USD 18.6 billion in 2025.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.3% during the forecast period of 2026 to 2035.
- The small and medium enterprises (SMEs) segment accounts for ~39% of the global zero trust architecture market in 2025, driven by increasing cyberattack risks, rising cloud adoption, and limited in-house IT security expertise.
- The increasing focus on identity- and access-oriented security models is propelling zero trust implementation, facilitating ongoing verification of users and devices.
- Risk evaluation driven by AI, analysis of behavior, and micro-segmentation enhance threat prevention in healthcare, IT, and manufacturing industries.
- The global zero-trust-architecture-market is highly consolidated, with the top five players accounting for nearly 60% of the market share in 2025.
- In February 2025, Microsoft enhanced its Entra platform with Adaptive Zero Trust Access Controls, which added continuous risk assessment to identities, devices, and workloads.
- In August 2025, IBM introduced new policy automation for Zero Trust within IBM Security Verify.
- Global Zero Trust Architecture Market is likely to create the total forecasting opportunity of USD 52.2 Bn till 2035
- North America is most attractive region, due to robust cybersecurity policies, and are rapidly modernizing their cloud adoption.
- To meet strict data protection and cybersecurity regulations that are growing in prevalence across the world, organizations must adopt advanced identity and access systems. A zero-trust architecture (ZTA) that accomplishes continuous verification of identities and devices is one-way organizations can fulfill these compliance requirements.
- In their national strategies and regulations for cybersecurity, governments and regulators are increasingly encouraging or even mandating that organizations adopt zero trust principles, making zero trust architecture a viable option for organizations that want to achieve the core function rather than just a feature of a system.
- The shift to hybrid cloud environments and remote work is another factor that drives the need for identity-first security: continuous authentication, device posture validation and behavioral checks were once optional but is becoming a necessity for highly regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and government.
- More and more enterprise organizations are viewing zero trust architecture as a timely option to reduce cyber risks as they increase operational resilience and prepare for security breaches increases which is expected to not only cause financial losses but can also damage reputation and erosion of customer trust.
- Deployment of Zero Trust typically requires a paradigm shift in systems: legacy systems often do not support the identity-access tools, micro-segmentation, or continuous monitoring required to make implementations and integrations both efficient and cost-effective. Adoption rates stall due to the high up-front costs, the impact of a shortage of applicable skill sets, and the behavioral hesitancy for organizations to change the processes - especially for small to medium enterprises.
- Operationalizing fine-grained trust policies (e.g., micro-segmentation) to design, build, and manage, particularly with hybrid or multi-cloud environments for scaling, is a difficult management task.
- It is often difficult for organizations to align their existing IT processes, security policies, and compliance audits with their goals of adopting zero trust; thus, they stall further and present a resource scarcity.
- What began as an almost fad-like security concept in developed countries is now rapidly becoming the norm in Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, where the triad of increased cyber security threats, legislative reforms, and cloud adoption are leading to zero trust. As the first step, governments are investing with technology vendors in the creation of identity infrastructures that are zero trust-ready and is expected to allow them to securely provide services not only to citizens, but to agencies and critical infrastructures as well.
- Further, with micro-segmentation, IDaaS, and cloud-native ZTNA solutions at the ready, Zero Trust technology vendors have a springboard that includes regulatory landscapes and a journey down digital transformation requiring urgency - especially in the regions.
- Public Private Partnerships in the less-developed areas build a cooperative landscape where enterprises can collaborate and create secure platforms, accelerate cloud migration, and integrate compliance frameworks with zero trust solutions.
- Micro-segmentation is gaining traction as a key strategic capability. By isolating workloads and enforcing "Never Trust, Always Verify" security policies within the organization's network, enterprises can curtail the opportunity for lateral attack. The identity-centric security model continues evolving. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), continuous identity verification, and behavior biometrics is expected to be introduced to enhance security measures around access control.
- Automation and orchestration is expected to become increasingly common. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is expected to be employed to improve policy enforcement, threat detection, and remedial actions, thereby relieving some of the workload associated with security operations.
- Zero Trust is moving away from IT environments and into OT/ICS environments. Various industrial networks, critical infrastructures, and operational technology are moving to ZT architecture to protect their environments. Additionally, when combined with threat intelligence platforms and security analytics, organizations is expected to provide the potential to foresee attacks, respond quicker, and deploy adaptable policies based on real-time risk object scores.
- SMEs are the quickest to implement zero trust architectures among other sectors. They are mainly influenced by the occurrences of ransomware, credential theft, and supply-chain attacks. These attacks take advantage of their limited security resources. Thus, as smaller businesses broaden their cloud usage, embrace remote work, and adopt SaaS, the necessity for continuous verification and least-privilege controls escalates.
- In the U.S., the collaboration of various factors such as CISA’s Zero Trust Maturity Model, the NIST SP 800-207 ZTA framework, and the increased use of multi-factor authentication, continuous verification, and micro-segmentation have led SMEs to upgrade their security that is still based on a perimeter. In the same manner, small enterprises in the EU are implementing ZTA to meet the requirements of the NIS2 Directive that sets more rigorous cyber security standards for essential and important entities, many of which belong to the SME sector.
- By rapidly switching to cloud-native security tools, automated configuration management, and identity governance platforms, SMEs have also made these solutions affordable and easy to deploy since, smaller businesses that are less capable of supporting a full in-house security operation. One of the major factors that were responsible for the rise of the zero-trust architecture was the increase in risk due to the extensive use of third-party vendors, distributed workforces, and digital collaboration platforms.
- Therefore, increasing digitization of their operations, growing dependence on third-party platforms, and rising vulnerability to modern cyber-attacks, SMEs have become a significant driving force for the worldwide zero trust market expansion.
- The United States is at the forefront of the global zero trust architecture market in the North America region. The countries have robust cybersecurity policies, and are rapidly modernizing their cloud adoption. The Zero Trust Maturity Model 2.0 developed by CISA is a key part of improving U.S. based enterprises as well as federal agencies to the next level of security focused on identity, continuous verification, and micro-segmented network architecture, thus establishing the U.S. as the leader in the region.
- Collaboration across industry is a key driver of the increased implementation of measures. Microsoft, Google Cloud, Cisco, Palo Alto Networks, and CrowdStrike collaborate with federal agencies to implement AI-driven threat analytics, identity governance, and cloud-based access control for critical Infrastructure and commercial sectors.
- Canada is committed to rapid implementation of national zero-trust initiatives and is collaborating with modernization of the federal cybersecurity frameworks as well as CCCS programs which focus on identity assurance, continuous monitoring, and secure inter-agency data sharing.
- Due to continually increasing cyber threats and investments in AI-enabled SOCs and other cloud-native controls, North America continues to set the global standard for zero trust maturity, regulatory coordination, and enterprise security modernization.
- In February 2025, Microsoft enhanced its Entra platform with Adaptive Zero Trust Access Controls, which added continuous risk assessment to identities, devices, and workloads. This update brought advanced anomaly scoring to access policies and AI-enabled session monitoring that automatically restricted or elevated permissions in real time. This release built on identity-based Zero Trust enforcement for enterprises migrating high-volume authentication workloads to Azure AD and Entra ID.
- In August 2025, IBM introduced new policy automation for Zero Trust within IBM Security Verify. This new capability enabled organizations to map dynamic access policies across hybrid cloud, mainframe, and multi-cloud environments with automated entitlement discovery, context-aware MFA orchestration, and IBM's AI models for risk-adaptive access checks to reduce unintended policy drift, close identity gaps, and improve alignment with federal zero trust standards.
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Nordic Countries
- Poland
- Russia & CIS
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia and New Zealand
- Indonesia
- Malaysia
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Turkey
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- Israel
- South Africa
- Egypt
- Nigeria
- Algeria
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Akamai Technologies, Inc.
- BeyondTrust (BeyondTrust Software, Inc.)
- Zscaler, Inc.
- Broadcom Inc. (Symantec Enterprise)
- Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- Okta, Inc.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc.
- CyberArk Software Ltd.
- Rapid7, Inc.
- Fortinet, Inc.
- Google LLC (Google Cloud)
- International Business Machines Corporation (IBM)
- Microsoft Corporation
- Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- Ping Identity Corporation
- Proofpoint, Inc.
- VMware, Inc.
- Rapid7, Inc.
- SailPoint Technologies Holdings, Inc.
- Thales Group
- Others Key Players
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Privileged Access Management (PAM)
- Network Segmentation / Microsegmentation
- Secure Web Gateways (SWG)
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
- Endpoint Security / EDR
- Policy Engine and Analytics
- Others
- Cloud-Based
- On-Premises
- Hybrid
- Identity-Centric Zero Trust Solutions
- Network-Centric Zero Trust Solutions
- Device-Centric Zero Trust Solutions
- Application-Centric Zero Trust Solutions
- Data-Centric Zero Trust Solutions
- Others
- Passwordless Authentication
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Continuous Authentication and Behavioral Biometrics
- Risk-based Adaptive Access
- Others
- Large Enterprises
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- Public Sector / Government Agencies
- Edge / Perimeter Enforcement
- Cloud Workload Enforcement
- Endpoint Enforcement
- Application-level Enforcement
- Data-level Enforcement
- Others
- Remote / Hybrid Workforce Secure Access
- Cloud Migration and Secure Cloud Access
- Secure DevOps and DevSecOps Workloads
- Third-Party / Supplier Access Management
- Protection of Critical Infrastructure and OT
- Others
- Integration with SIEM and SOAR
- Integration with SASE / Secure Access Service Edge
- Integration with PAM and IAM ecosystems
- Integration with Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR)
- Others
- Banking, Financial Services & Insurance (BFSI)
- Healthcare & Life Sciences
- Government & Defense
- IT & Telecommunications
- Retail & E-commerce
- Energy & Utilities
- Manufacturing
- Education
- Others
- 1. Research Methodology and Assumptions
- 1.1. Definitions
- 1.2. Research Design and Approach
- 1.3. Data Collection Methods
- 1.4. Base Estimates and Calculations
- 1.5. Forecasting Models
- 1.5.1. Key Forecast Factors & Impact Analysis
- 1.6. Secondary Research
- 1.6.1. Open Sources
- 1.6.2. Paid Databases
- 1.6.3. Associations
- 1.7. Primary Research
- 1.7.1. Primary Sources
- 1.7.2. Primary Interviews with Stakeholders across Ecosystem
- 2. Executive Summary
- 2.1. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Outlook
- 2.1.1. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 2.1.2. Compounded Annual Growth Rate Analysis
- 2.1.3. Growth Opportunity Analysis
- 2.1.4. Segmental Share Analysis
- 2.1.5. Geographical Share Analysis
- 2.2. Market Analysis and Facts
- 2.3. Supply-Demand Analysis
- 2.4. Competitive Benchmarking
- 2.5. Go-to- Market Strategy
- 2.5.1. Customer/ End-use Industry Assessment
- 2.5.2. Growth Opportunity Data, 2026-2035
- 2.5.2.1. Regional Data
- 2.5.2.2. Country Data
- 2.5.2.3. Segmental Data
- 2.5.3. Identification of Potential Market Spaces
- 2.5.4. GAP Analysis
- 2.5.5. Potential Attractive Price Points
- 2.5.6. Prevailing Market Risks & Challenges
- 2.5.7. Preferred Sales & Marketing Strategies
- 2.5.8. Key Recommendations and Analysis
- 2.5.9. A Way Forward
- 2.1. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Outlook
- 3. Industry Data and Premium Insights
- 3.1. Global Information Technology & Media Ecosystem Overview, 2025
- 3.1.1. Information Technology & Media Industry Analysis
- 3.1.2. Key Trends for Information Technology & Media Industry
- 3.1.3. Regional Distribution for Information Technology & Media Industry
- 3.2. Supplier Customer Data
- 3.3. Technology Roadmap and Developments
- 3.1. Global Information Technology & Media Ecosystem Overview, 2025
- 4. Market Overview
- 4.1. Market Dynamics
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.1.1.1. Rising demand for secure, identity-centric access and continuous verification across enterprise networks
- 4.1.1.2. Growing adoption of AI- and ML-driven access management, threat detection, and policy enforcement solutions
- 4.1.1.3. Increasing regulatory requirements for data privacy, cybersecurity frameworks, and compliance
- 4.1.2. Restraints
- 4.1.2.1. High deployment and operational costs of zero trust infrastructure, tools, and identity management solutions
- 4.1.2.2. Challenges in integrating zero trust frameworks with legacy IT systems, cloud environments, and diverse network architectures
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.2. Key Trend Analysis
- 4.3. Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1. Key Regulations, Norms, and Subsidies, by Key Countries
- 4.3.2. Tariffs and Standards
- 4.3.3. Impact Analysis of Regulations on the Market
- 4.4. Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4.1. Component Suppliers/ Device Suppliers
- 4.4.2. System Integrators/ Technology Providers
- 4.4.3. Zero Trust Architecture Solution Providers
- 4.4.4. End Users
- 4.5. Cost Structure Analysis
- 4.5.1. Parameter’s Share for Cost Associated
- 4.5.2. COGP vs COGS
- 4.5.3. Profit Margin Analysis
- 4.6. Pricing Analysis
- 4.6.1. Regional Pricing Analysis
- 4.6.2. Segmental Pricing Trends
- 4.6.3. Factors Influencing Pricing
- 4.7. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8. PESTEL Analysis
- 4.9. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Demand
- 4.9.1. Historical Market Size –Value (US$ Bn), 2020-2024
- 4.9.2. Current and Future Market Size –Value (US$ Bn), 2026–2035
- 4.9.2.1. Y-o-Y Growth Trends
- 4.9.2.2. Absolute $ Opportunity Assessment
- 4.1. Market Dynamics
- 5. Competition Landscape
- 5.1. Competition structure
- 5.1.1. Fragmented v/s consolidated
- 5.2. Company Share Analysis, 2025
- 5.2.1. Global Company Market Share
- 5.2.2. By Region
- 5.2.2.1. North America
- 5.2.2.2. Europe
- 5.2.2.3. Asia Pacific
- 5.2.2.4. Middle East
- 5.2.2.5. Africa
- 5.2.2.6. South America
- 5.3. Product Comparison Matrix
- 5.3.1. Specifications
- 5.3.2. Market Positioning
- 5.3.3. Pricing
- 5.1. Competition structure
- 6. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis, by Component
- 6.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 6.2. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Component, 2021-2035
- 6.2.1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- 6.2.2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- 6.2.3. Privileged Access Management (PAM)
- 6.2.4. Network Segmentation / Microsegmentation
- 6.2.5. Secure Web Gateways (SWG)
- 6.2.6. Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
- 6.2.7. Endpoint Security / EDR
- 6.2.8. Policy Engine and Analytics
- 6.2.9. Others
- 7. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis, by Deployment Mode
- 7.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 7.2. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Deployment Mode, 2021-2035
- 7.2.1. Cloud-Based
- 7.2.2. On-Premises
- 7.2.3. Hybrid
- 8. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis, by Solution Type
- 8.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 8.2. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Solution Type, 2021-2035
- 8.2.1. Identity-Centric Zero Trust Solutions
- 8.2.2. Network-Centric Zero Trust Solutions
- 8.2.3. Device-Centric Zero Trust Solutions
- 8.2.4. Application-Centric Zero Trust Solutions
- 8.2.5. Data-Centric Zero Trust Solutions
- 8.2.6. Others
- 9. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis, by Authentication & Access Method
- 9.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 9.2. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Authentication & Access Method, 2021-2035
- 9.2.1. Passwordless Authentication
- 9.2.2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- 9.2.3. Continuous Authentication and Behavioral Biometrics
- 9.2.4. Risk-based Adaptive Access
- 9.2.5. Others
- 10. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis, by Enterprise Size
- 10.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 10.2. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Enterprise Size, 2021-2035
- 10.2.1. Large Enterprises
- 10.2.2. Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- 10.2.3. Public Sector / Government Agencies
- 11. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis, by Enforcement Point
- 11.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 11.2. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Enforcement Point, 2021-2035
- 11.2.1. Edge / Perimeter Enforcement
- 11.2.2. Cloud Workload Enforcement
- 11.2.3. Endpoint Enforcement
- 11.2.4. Application-level Enforcement
- 11.2.5. Data-level Enforcement
- 11.2.6. Others
- 12. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis, by Use Case / Application
- 12.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 12.2. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Use Case / Application, 2021-2035
- 12.2.1. Remote / Hybrid Workforce Secure Access
- 12.2.2. Cloud Migration and Secure Cloud Access
- 12.2.3. Secure DevOps and DevSecOps Workloads
- 12.2.4. Third-Party / Supplier Access Management
- 12.2.5. Protection of Critical Infrastructure and OT
- 12.2.6. Others
- 13. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis, by Technology Integration
- 13.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 13.2. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Technology Integration, 2021-2035
- 13.2.1. Integration with SIEM and SOAR
- 13.2.2. Integration with SASE / Secure Access Service Edge
- 13.2.3. Integration with PAM and IAM ecosystems
- 13.2.4. Integration with Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR)
- 13.2.5. Others
- 14. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis, by Industry Vertical
- 14.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 14.2. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Industry Vertical, 2021-2035
- 14.2.1. Banking, Financial Services & Insurance (BFSI)
- 14.2.2. Healthcare & Life Sciences
- 14.2.3. Government & Defense
- 14.2.4. IT & Telecommunications
- 14.2.5. Retail & E-commerce
- 14.2.6. Energy & Utilities
- 14.2.7. Manufacturing
- 14.2.8. Education
- 14.2.9. Others
- 15. Global Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis and Forecasts, by Region
- 15.1. Key Findings
- 15.2. Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, by Region, 2021-2035
- 15.2.1. North America
- 15.2.2. Europe
- 15.2.3. Asia Pacific
- 15.2.4. Middle East
- 15.2.5. Africa
- 15.2.6. South America
- 16. North America Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis
- 16.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 16.2. Regional Snapshot
- 16.3. North America Zero Trust Architecture Market Size Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 16.3.1. Component
- 16.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 16.3.3. Solution Type
- 16.3.4. Authentication & Access Method
- 16.3.5. Enterprise Size
- 16.3.6. Enforcement Point
- 16.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 16.3.8. Technology Integration
- 16.3.9. Industry Vertical
- 16.3.10. Country
- 16.3.10.1. USA
- 16.3.10.2. Canada
- 16.3.10.3. Mexico
- 16.4. USA Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 16.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.4.2. Component
- 16.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.4.4. Solution Type
- 16.4.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 16.4.6. Enterprise Size
- 16.4.7. Enforcement Point
- 16.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.4.9. Technology Integration
- 16.4.10. Industry Vertical
- 16.5. Canada Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 16.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.5.2. Component
- 16.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.5.4. Solution Type
- 16.5.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 16.5.6. Enterprise Size
- 16.5.7. Enforcement Point
- 16.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.5.9. Technology Integration
- 16.5.10. Industry Vertical
- 16.6. Mexico Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 16.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 16.6.2. Component
- 16.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 16.6.4. Solution Type
- 16.6.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 16.6.6. Enterprise Size
- 16.6.7. Enforcement Point
- 16.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 16.6.9. Technology Integration
- 16.6.10. Industry Vertical
- 17. Europe Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis
- 17.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 17.2. Regional Snapshot
- 17.3. Europe Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 17.3.1. Component
- 17.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 17.3.3. Solution Type
- 17.3.4. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.3.5. Enterprise Size
- 17.3.6. Enforcement Point
- 17.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 17.3.8. Technology Integration
- 17.3.9. Industry Vertical
- 17.3.10. Country
- 17.3.10.1. Germany
- 17.3.10.2. United Kingdom
- 17.3.10.3. France
- 17.3.10.4. Italy
- 17.3.10.5. Spain
- 17.3.10.6. Netherlands
- 17.3.10.7. Nordic Countries
- 17.3.10.8. Poland
- 17.3.10.9. Russia & CIS
- 17.3.10.10. Rest of Europe
- 17.4. Germany Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 17.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.4.2. Component
- 17.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.4.4. Solution Type
- 17.4.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.4.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.4.7. Enforcement Point
- 17.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.4.9. Technology Integration
- 17.4.10. Industry Vertical
- 17.5. United Kingdom Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 17.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.5.2. Component
- 17.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.5.4. Solution Type
- 17.5.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.5.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.5.7. Enforcement Point
- 17.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.5.9. Technology Integration
- 17.5.10. Industry Vertical
- 17.6. France Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 17.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.6.2. Component
- 17.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.6.4. Solution Type
- 17.6.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.6.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.6.7. Enforcement Point
- 17.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.6.9. Technology Integration
- 17.6.10. Industry Vertical
- 17.7. Italy Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 17.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.7.2. Component
- 17.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.7.4. Solution Type
- 17.7.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.7.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.7.7. Enforcement Point
- 17.7.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.7.9. Technology Integration
- 17.7.10. Industry Vertical
- 17.8. Spain Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 17.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.8.2. Component
- 17.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.8.4. Solution Type
- 17.8.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.8.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.8.7. Enforcement Point
- 17.8.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.8.9. Technology Integration
- 17.8.10. Industry Vertical
- 17.9. Netherlands Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 17.9.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.9.2. Component
- 17.9.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.9.4. Solution Type
- 17.9.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.9.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.9.7. Enforcement Point
- 17.9.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.9.9. Technology Integration
- 17.9.10. Industry Vertical
- 17.10. Nordic Countries Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 17.10.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.10.2. Component
- 17.10.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.10.4. Solution Type
- 17.10.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.10.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.10.7. Enforcement Point
- 17.10.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.10.9. Technology Integration
- 17.10.10. Industry Vertical
- 17.11. Poland Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 17.11.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.11.2. Component
- 17.11.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.11.4. Solution Type
- 17.11.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.11.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.11.7. Enforcement Point
- 17.11.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.11.9. Technology Integration
- 17.11.10. Industry Vertical
- 17.12. Russia & CIS Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 17.12.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.12.2. Component
- 17.12.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.12.4. Solution Type
- 17.12.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.12.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.12.7. Enforcement Point
- 17.12.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.12.9. Technology Integration
- 17.12.10. Industry Vertical
- 17.13. Rest of Europe Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 17.13.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 17.13.2. Component
- 17.13.3. Deployment Mode
- 17.13.4. Solution Type
- 17.13.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 17.13.6. Enterprise Size
- 17.13.7. Enforcement Point
- 17.13.8. Use Case / Application
- 17.13.9. Technology Integration
- 17.13.10. Industry Vertical
- 18. Asia Pacific Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis
- 18.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 18.2. Regional Snapshot
- 18.3. Asia Pacific Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 18.3.1. Component
- 18.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 18.3.3. Solution Type
- 18.3.4. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.3.5. Enterprise Size
- 18.3.6. Enforcement Point
- 18.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 18.3.8. Technology Integration
- 18.3.9. Industry Vertical
- 18.3.10. Country
- 18.3.10.1. China
- 18.3.10.2. India
- 18.3.10.3. Japan
- 18.3.10.4. South Korea
- 18.3.10.5. Australia and New Zealand
- 18.3.10.6. Indonesia
- 18.3.10.7. Malaysia
- 18.3.10.8. Thailand
- 18.3.10.9. Vietnam
- 18.3.10.10. Rest of Asia Pacific
- 18.4. China Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 18.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.4.2. Component
- 18.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.4.4. Solution Type
- 18.4.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.4.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.4.7. Enforcement Point
- 18.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.4.9. Technology Integration
- 18.4.10. Industry Vertical
- 18.5. India Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 18.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.5.2. Component
- 18.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.5.4. Solution Type
- 18.5.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.5.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.5.7. Enforcement Point
- 18.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.5.9. Technology Integration
- 18.5.10. Industry Vertical
- 18.6. Japan Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 18.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.6.2. Component
- 18.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.6.4. Solution Type
- 18.6.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.6.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.6.7. Enforcement Point
- 18.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.6.9. Technology Integration
- 18.6.10. Industry Vertical
- 18.7. South Korea Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 18.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.7.2. Component
- 18.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.7.4. Solution Type
- 18.7.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.7.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.7.7. Enforcement Point
- 18.7.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.7.9. Technology Integration
- 18.7.10. Industry Vertical
- 18.8. Australia and New Zealand Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 18.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.8.2. Component
- 18.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.8.4. Solution Type
- 18.8.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.8.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.8.7. Enforcement Point
- 18.8.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.8.9. Technology Integration
- 18.8.10. Industry Vertical
- 18.9. Indonesia Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 18.9.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.9.2. Component
- 18.9.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.9.4. Solution Type
- 18.9.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.9.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.9.7. Enforcement Point
- 18.9.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.9.9. Technology Integration
- 18.9.10. Industry Vertical
- 18.10. Malaysia Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 18.10.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.10.2. Component
- 18.10.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.10.4. Solution Type
- 18.10.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.10.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.10.7. Enforcement Point
- 18.10.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.10.9. Technology Integration
- 18.10.10. Industry Vertical
- 18.11. Thailand Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 18.11.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.11.2. Component
- 18.11.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.11.4. Solution Type
- 18.11.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.11.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.11.7. Enforcement Point
- 18.11.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.11.9. Technology Integration
- 18.11.10. Industry Vertical
- 18.12. Vietnam Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 18.12.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.12.2. Component
- 18.12.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.12.4. Solution Type
- 18.12.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.12.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.12.7. Enforcement Point
- 18.12.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.12.9. Technology Integration
- 18.12.10. Industry Vertical
- 18.13. Rest of Asia Pacific Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 18.13.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 18.13.2. Component
- 18.13.3. Deployment Mode
- 18.13.4. Solution Type
- 18.13.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 18.13.6. Enterprise Size
- 18.13.7. Enforcement Point
- 18.13.8. Use Case / Application
- 18.13.9. Technology Integration
- 18.13.10. Industry Vertical
- 19. Middle East Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis
- 19.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 19.2. Regional Snapshot
- 19.3. Middle East Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 19.3.1. Component
- 19.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 19.3.3. Solution Type
- 19.3.4. Authentication & Access Method
- 19.3.5. Enterprise Size
- 19.3.6. Enforcement Point
- 19.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 19.3.8. Technology Integration
- 19.3.9. Industry Vertical
- 19.3.10. Country
- 19.3.10.1. Turkey
- 19.3.10.2. UAE
- 19.3.10.3. Saudi Arabia
- 19.3.10.4. Israel
- 19.3.10.5. Rest of Middle East
- 19.4. Turkey Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 19.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.4.2. Component
- 19.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.4.4. Solution Type
- 19.4.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 19.4.6. Enterprise Size
- 19.4.7. Enforcement Point
- 19.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 19.4.9. Technology Integration
- 19.4.10. Industry Vertical
- 19.5. UAE Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 19.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.5.2. Component
- 19.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.5.4. Solution Type
- 19.5.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 19.5.6. Enterprise Size
- 19.5.7. Enforcement Point
- 19.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 19.5.9. Technology Integration
- 19.5.10. Industry Vertical
- 19.6. Saudi Arabia Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 19.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.6.2. Component
- 19.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.6.4. Solution Type
- 19.6.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 19.6.6. Enterprise Size
- 19.6.7. Enforcement Point
- 19.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 19.6.9. Technology Integration
- 19.6.10. Industry Vertical
- 19.7. Israel Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 19.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.7.2. Component
- 19.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.7.4. Solution Type
- 19.7.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 19.7.6. Enterprise Size
- 19.7.7. Enforcement Point
- 19.7.8. Use Case / Application
- 19.7.9. Technology Integration
- 19.7.10. Industry Vertical
- 19.8. Rest of Middle East Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 19.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 19.8.2. Component
- 19.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 19.8.4. Solution Type
- 19.8.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 19.8.6. Enterprise Size
- 19.8.7. Enforcement Point
- 19.8.8. Use Case / Application
- 19.8.9. Technology Integration
- 19.8.10. Industry Vertical
- 20. Africa Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis
- 20.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 20.2. Regional Snapshot
- 20.3. Africa Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 20.3.1. Component
- 20.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 20.3.3. Solution Type
- 20.3.4. Authentication & Access Method
- 20.3.5. Enterprise Size
- 20.3.6. Enforcement Point
- 20.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 20.3.8. Technology Integration
- 20.3.9. Industry Vertical
- 20.3.10. Country
- 20.3.10.1. South Africa
- 20.3.10.2. Egypt
- 20.3.10.3. Nigeria
- 20.3.10.4. Algeria
- 20.3.10.5. Rest of Africa
- 20.4. South Africa Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 20.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.4.2. Component
- 20.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.4.4. Solution Type
- 20.4.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 20.4.6. Enterprise Size
- 20.4.7. Enforcement Point
- 20.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 20.4.9. Technology Integration
- 20.4.10. Industry Vertical
- 20.5. Egypt Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 20.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.5.2. Component
- 20.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.5.4. Solution Type
- 20.5.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 20.5.6. Enterprise Size
- 20.5.7. Enforcement Point
- 20.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 20.5.9. Technology Integration
- 20.5.10. Industry Vertical
- 20.6. Nigeria Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 20.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.6.2. Component
- 20.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.6.4. Solution Type
- 20.6.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 20.6.6. Enterprise Size
- 20.6.7. Enforcement Point
- 20.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 20.6.9. Technology Integration
- 20.6.10. Industry Vertical
- 20.7. Algeria Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 20.7.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.7.2. Component
- 20.7.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.7.4. Solution Type
- 20.7.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 20.7.6. Enterprise Size
- 20.7.7. Enforcement Point
- 20.7.8. Use Case / Application
- 20.7.9. Technology Integration
- 20.7.10. Industry Vertical
- 20.8. Rest of Africa Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 20.8.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 20.8.2. Component
- 20.8.3. Deployment Mode
- 20.8.4. Solution Type
- 20.8.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 20.8.6. Enterprise Size
- 20.8.7. Enforcement Point
- 20.8.8. Use Case / Application
- 20.8.9. Technology Integration
- 20.8.10. Industry Vertical
- 21. South America Zero Trust Architecture Market Analysis
- 21.1. Key Segment Analysis
- 21.2. Regional Snapshot
- 21.3. South America Zero Trust Architecture Market Size (Value - US$ Bn), Analysis, and Forecasts, 2021-2035
- 21.3.1. Component
- 21.3.2. Deployment Mode
- 21.3.3. Solution Type
- 21.3.4. Authentication & Access Method
- 21.3.5. Enterprise Size
- 21.3.6. Enforcement Point
- 21.3.7. Use Case / Application
- 21.3.8. Technology Integration
- 21.3.9. Industry Vertical
- 21.3.10. Country
- 21.3.10.1. Brazil
- 21.3.10.2. Argentina
- 21.3.10.3. Rest of South America
- 21.4. Brazil Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 21.4.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 21.4.2. Component
- 21.4.3. Deployment Mode
- 21.4.4. Solution Type
- 21.4.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 21.4.6. Enterprise Size
- 21.4.7. Enforcement Point
- 21.4.8. Use Case / Application
- 21.4.9. Technology Integration
- 21.4.10. Industry Vertical
- 21.5. Argentina Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 21.5.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 21.5.2. Component
- 21.5.3. Deployment Mode
- 21.5.4. Solution Type
- 21.5.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 21.5.6. Enterprise Size
- 21.5.7. Enforcement Point
- 21.5.8. Use Case / Application
- 21.5.9. Technology Integration
- 21.5.10. Industry Vertical
- 21.6. Rest of South America Zero Trust Architecture Market
- 21.6.1. Country Segmental Analysis
- 21.6.2. Component
- 21.6.3. Deployment Mode
- 21.6.4. Solution Type
- 21.6.5. Authentication & Access Method
- 21.6.6. Enterprise Size
- 21.6.7. Enforcement Point
- 21.6.8. Use Case / Application
- 21.6.9. Technology Integration
- 21.6.10. Industry Vertical
- 22. Key Players/ Company Profile
- 22.1. Akamai Technologies, Inc.
- 22.1.1. Company Details/ Overview
- 22.1.2. Company Financials
- 22.1.3. Key Customers and Competitors
- 22.1.4. Business/ Industry Portfolio
- 22.1.5. Product Portfolio/ Specification Details
- 22.1.6. Pricing Data
- 22.1.7. Strategic Overview
- 22.1.8. Recent Developments
- 22.2. BeyondTrust (BeyondTrust Software, Inc.)
- 22.3. Broadcom Inc. (Symantec Enterprise)
- 22.4. Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- 22.5. Cisco Systems, Inc.
- 22.6. CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc.
- 22.7. CyberArk Software Ltd.
- 22.8. Fortinet, Inc.
- 22.9. Google LLC (Google Cloud)
- 22.10. International Business Machines Corporation (IBM)
- 22.11. Microsoft Corporation
- 22.12. Okta, Inc.
- 22.13. Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- 22.14. Ping Identity Corporation
- 22.15. Proofpoint, Inc.
- 22.16. Rapid7, Inc.
- 22.17. SailPoint Technologies Holdings, Inc.
- 22.18. Thales Group
- 22.19. VMware, Inc.
- 22.20. Zscaler, Inc.
- 22.21. Others Key Players
- 22.1. Akamai Technologies, Inc.
- Company websites, annual reports, financial reports, broker reports, and investor presentations
- National government documents, statistical databases and reports
- News articles, press releases and web-casts specific to the companies operating in the market, Magazines, reports, and others
- We gather information from commercial data sources for deriving company specific data such as segmental revenue, share for geography, product revenue, and others
- Internal and external proprietary databases (industry-specific), relevant patent, and regulatory databases
- Governing Bodies, Government Organizations
- Relevant Authorities, Country-specific Associations for Industries
- Historical Trends – Past market patterns, cycles, and major events that shaped how markets behave over time. Understanding past trends helps predict future behavior.
- Industry Factors – Specific characteristics of the industry like structure, regulations, and innovation cycles that affect market dynamics.
- Macroeconomic Factors – Economic conditions like GDP growth, inflation, and employment rates that affect how much money people have to spend.
- Demographic Factors – Population characteristics like age, income, and location that determine who can buy your product.
- Technology Factors – How quickly people adopt new technology and how much technology infrastructure exists.
- Regulatory Factors – Government rules, laws, and policies that can help or restrict market growth.
- Competitive Factors – Analyzing competition structure such as degree of competition and bargaining power of buyers and suppliers.
- Identify and quantify factors that drive market changes
- Statistical modeling to establish relationships between market drivers and outcomes
- Understand regular cyclical patterns in market demand
- Advanced statistical techniques to separate trend, seasonal, and irregular components
- Identify underlying market growth patterns and momentum
- Statistical analysis of historical data to project future trends
- Gather deep industry insights and contextual understanding
- In-depth interviews with key industry stakeholders
- Prepare for uncertainty by modeling different possible futures
- Creating optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely scenarios
- Sophisticated forecasting for complex time series data
- Auto-regressive integrated moving average models with seasonal components
- Apply economic theory to market forecasting
- Sophisticated economic models that account for market interactions
- Harness collective wisdom of industry experts
- Structured, multi-round expert consultation process
- Quantify uncertainty and probability distributions
- Thousands of simulations with varying input parameters
- Data Source Triangulation – Using multiple data sources to examine the same phenomenon
- Methodological Triangulation – Using multiple research methods to study the same research question
- Investigator Triangulation – Using multiple researchers or analysts to examine the same data
- Theoretical Triangulation – Using multiple theoretical perspectives to interpret the same data
Zero Trust Architecture Market by Component, Deployment Mode, Solution Type, Authentication & Access Method, Enterprise Size, Enforcement Point, Use Case / Application, Technology Integration, Industry Vertical and Geography
Insightified
Mid-to-large firms spend $20K–$40K quarterly on systematic research and typically recover multiples through improved growth and profitability
Research is no longer optional. Leading firms use it to uncover $10M+ in hidden revenue opportunities annually
Our research-consulting programs yields measurable ROI: 20–30% revenue increases from new markets, 11% profit upticks from pricing, and 20–30% cost savings from operations
Zero Trust Architecture Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Component (Identity and Access Management (IAM), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Privileged Access Management (PAM), Network Segmentation / Microsegmentation, Secure Web Gateways (SWG), Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), Endpoint Security / EDR, Policy Engine and Analytics, Others), Deployment Mode, Solution Type, Authentication & Access Method, Enterprise Size, Enforcement Point, Use Case / Application, Technology Integration, Industry Vertical and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, Africa, and South America) – Global Industry Data, Trends, and Forecasts, 2026–2035
|
Market Structure & Evolution |
|
|
Segmental Data Insights |
|
|
Demand Trends |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Strategic Development |
|
|
Future Outlook & Opportunities |
|
Zero Trust Architecture Market Size, Share, and Growth
The global zero trust architecture market is experiencing robust growth, with its estimated value of USD 18.6 billion in the year 2025 and USD 70.8 billion by the period 2035, registering a CAGR of 14.3% during the forecast period. Global zero trust architecture market is growing rapidly and it is supported by three main factors: increasing cyber-attack sophistication, very strict regulatory compliance, and migration on a large scale to cloud-native environments.

Todd Palmer, Senior Vice President, Global Partner Sales & Alliances at Illumio, stated, "If we consider only regulatory requirements, we are assisting companies in moving away the idea of breaches as something terrible to the understanding that breaches is expected to happen inevitably. Our proposition supports the company in keeping the verification ongoing, making insider threats less likely, and improving the security level of the organization as a whole.”
Companies use zero trust approach more and more in order to be in line with data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other requirements. A recent notable instance, the U.S. Department of Defense is putting into practice its zero-trust framework, with an aim to have it completely operational by 2027 in order to secure sensitive defense networks. In the same way, the U.S. Navy cooperated with Microsoft and conducted experiments on extensive deployment of zero trust that was involving more than 560,000 identities and devices, and they achieved 100% of their target zero trust objectives.
The change to hybrid IT infrastructure and telecommuting has made access models highly dependent on identity and device the only viable ones. Federal civilian agencies have done a lot in the implementation of zero trust across identity, device posture, and network segmentation. All these events - regulatory pressure, cloud transformation, and AI-driven security - are the reasons supporting zero trust architecture market worldwide, thus allowing them to enforce least-privilege access, reduce risk, and raise their level of resilience.
Moreover, the global zero trust architecture market is full of possibilities nearby that can be easily recognized as platforms of AI-based threat detection, systems of real-time access monitoring, tools of behavioral analytics, solutions of micro-segmentation, and gateways of secure cloud access. Using these remote products, companies would be able not only to further strengthen network security but also to upgrade compliance and be more efficient in operations thus enabling them to implement zero trust frameworks in different sectors.

Zero Trust Architecture Market Dynamics and Trends
Driver: Tightening Regulatory Mandates Fueling Identity‑Centric Security
Restraint: Complexity and Legacy Infrastructure Hurdles Limiting Zero Trust Architecture Adoption
Opportunity: Expansion in Emerging Regions & Government‑Driven Zero Trust Initiatives
Key Trend: Biometrics, AI, Automation, and Micro‑Segmentation Driving Zero Trust Architecture Evolution
Zero-Trust-Architecture-Market Analysis and Segmental Data

“Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Lead Global Zero Trust Architecture Market amid Rising Cyberthreats and Expanding Digital Footprints"
“North America Leads Zero Trust Architecture Market with Advanced Cybersecurity Regulations and Rapid Cloud Modernization"
Zero-Trust-Architecture-Market Ecosystem
The zero trust architecture (ZTA) market is consolidating into a handful of large companies-Microsoft, Palo Alto Networks, Okta, Cisco, Zscaler, and CrowdStrike-due to their size, advanced research and development capabilities, and cloud-native platforms that position them well for widespread use by organizations worldwide. These organizations also differentiate themselves using a combination of inherent technologies focused on Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), identity fabrics, endpoint protection, and micro-segmentation, which allow organizations to transition from perimeter-based security to continuous verification compliance.
In addition to using new technologies with sustainable features, like AI-driven telemetry to inform behavioral analytics, automated policy orchestration, and managed zero trust architecture (ZTA) services that ease the adoption and reduce operational burden.
Government agencies and research organizations are also large influencers of market direction through setting standards as well as funding modernization efforts. For example, in September 2025, Okta announced new identity-fabric lifecycle management features designed to secure AI agents and integrate identity into enterprise workflows, thus clearing the path of identity-first zero trust architecture (ZTA). Likewise, the U. S. Navy's Flank Speed program accomplished several deliverables in zero trust compliance by the end of 2024, demonstrating verifiable advancements in cloud security and operational readiness.
Major players expand their product lines through acquisitions, integrated platforms and bundled security suites that improve productivity, enable deployment, and scale protection across hybrid and multi-cloud, thereby reinforcing the dual trends of market consolidation and technological progress.

Recent Development and Strategic Overview:
Report Scope
|
Attribute |
Detail |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 18.6 Bn |
|
Market Forecast Value in 2035 |
USD 70.8 Bn |
|
Growth Rate (CAGR) |
14.3% |
|
Forecast Period |
2026 – 2035 |
|
Historical Data Available for |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Market Size Units |
USD Bn for Value |
|
Report Format |
Electronic (PDF) + Excel |
|
Regions and Countries Covered |
|||||
|
North America |
Europe |
Asia Pacific |
Middle East |
Africa |
South America |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Companies Covered |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Zero-Trust-Architecture-Market Segmentation and Highlights
|
Segment |
Sub-segment |
|
Zero Trust Architecture Market, By Component |
|
|
Zero Trust Architecture Market, By Deployment Mode |
|
|
Zero Trust Architecture Market, By Solution Model |
|
|
Zero Trust Architecture Market, By Authentication & Access Method |
|
|
Zero Trust Architecture Market, By Enterprise Size |
|
|
Zero Trust Architecture Market, By Enforcement Point |
|
|
Zero Trust Architecture Market, By Use Case / Application |
|
|
Zero Trust Architecture Market, By Technology Integration |
|
|
Zero Trust Architecture Market, By Industry Vertical |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Table of Contents
Note* - This is just tentative list of players. While providing the report, we will cover more number of players based on their revenue and share for each geography
Research Design
Our research design integrates both demand-side and supply-side analysis through a balanced combination of primary and secondary research methodologies. By utilizing both bottom-up and top-down approaches alongside rigorous data triangulation methods, we deliver robust market intelligence that supports strategic decision-making.
MarketGenics' comprehensive research design framework ensures the delivery of accurate, reliable, and actionable market intelligence. Through the integration of multiple research approaches, rigorous validation processes, and expert analysis, we provide our clients with the insights needed to make informed strategic decisions and capitalize on market opportunities.
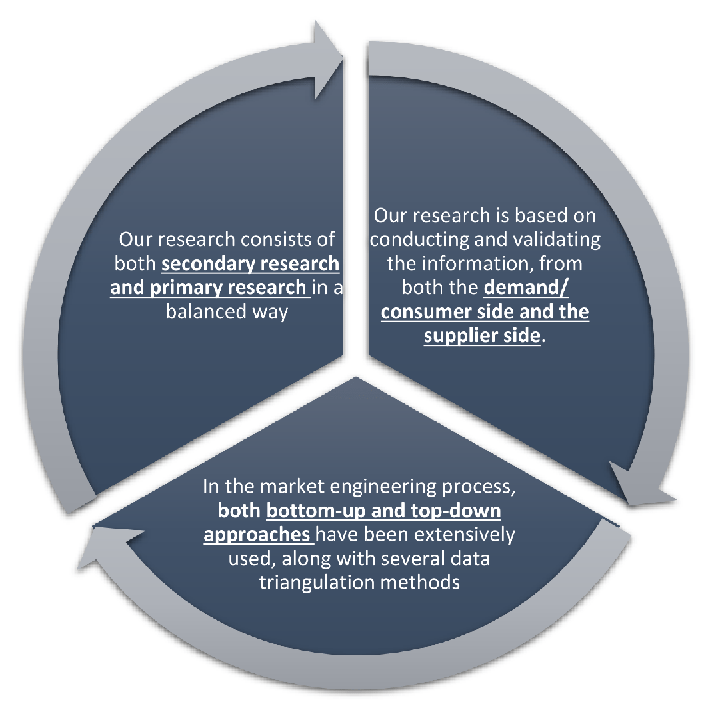
MarketGenics leverages a dedicated industry panel of experts and a comprehensive suite of paid databases to effectively collect, consolidate, and analyze market intelligence.
Our approach has consistently proven to be reliable and effective in generating accurate market insights, identifying key industry trends, and uncovering emerging business opportunities.
Through both primary and secondary research, we capture and analyze critical company-level data such as manufacturing footprints, including technical centers, R&D facilities, sales offices, and headquarters.
Our expert panel further enhances our ability to estimate market size for specific brands based on validated field-level intelligence.
Our data mining techniques incorporate both parametric and non-parametric methods, allowing for structured data collection, sorting, processing, and cleaning.
Demand projections are derived from large-scale data sets analyzed through proprietary algorithms, culminating in robust and reliable market sizing.
Research Approach
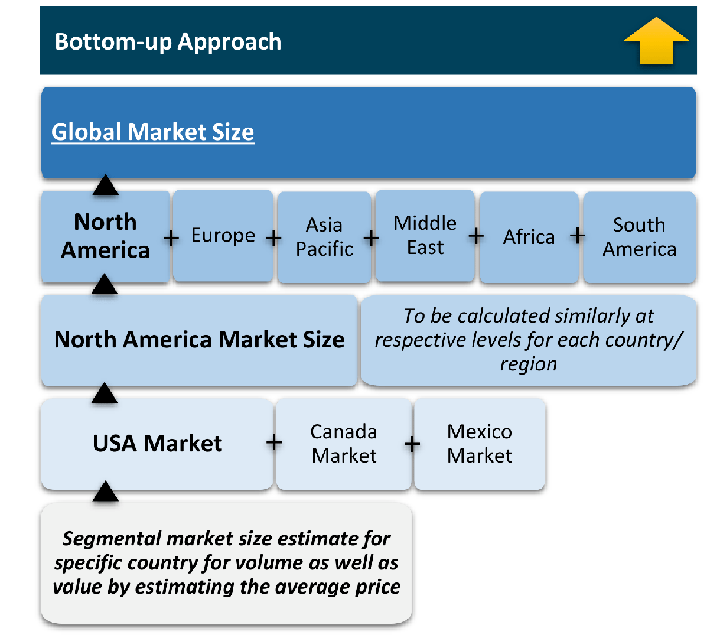
The bottom-up approach builds market estimates by starting with the smallest addressable market units and systematically aggregating them to create comprehensive market size projections.
This method begins with specific, granular data points and builds upward to create the complete market landscape.
Customer Analysis → Segmental Analysis → Geographical Analysis
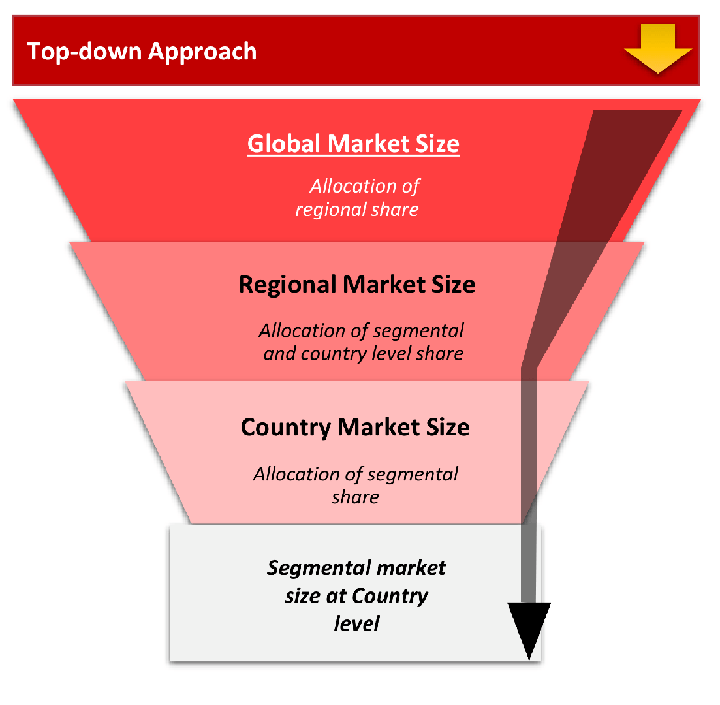
The top-down approach starts with the broadest possible market data and systematically narrows it down through a series of filters and assumptions to arrive at specific market segments or opportunities.
This method begins with the big picture and works downward to increasingly specific market slices.
TAM → SAM → SOM
Research Methods
Desk / Secondary Research
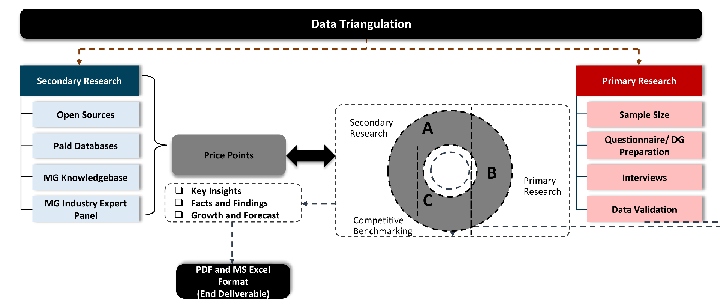
While analysing the market, we extensively study secondary sources, directories, and databases to identify and collect information useful for this technical, market-oriented, and commercial report. Secondary sources that we utilize are not only the public sources, but it is a combination of Open Source, Associations, Paid Databases, MG Repository & Knowledgebase, and others.
We also employ the model mapping approach to estimate the product level market data through the players' product portfolio
Primary Research
Primary research/ interviews is vital in analyzing the market. Most of the cases involves paid primary interviews. Primary sources include primary interviews through e-mail interactions, telephonic interviews, surveys as well as face-to-face interviews with the different stakeholders across the value chain including several industry experts.
| Type of Respondents | Number of Primaries |
|---|---|
| Tier 2/3 Suppliers | ~20 |
| Tier 1 Suppliers | ~25 |
| End-users | ~25 |
| Industry Expert/ Panel/ Consultant | ~30 |
| Total | ~100 |
MG Knowledgebase
• Repository of industry blog, newsletter and case studies
• Online platform covering detailed market reports, and company profiles
Forecasting Factors and Models
Forecasting Factors
Forecasting Models / Techniques
Multiple Regression Analysis
Time Series Analysis – Seasonal Patterns
Time Series Analysis – Trend Analysis
Expert Opinion – Expert Interviews
Multi-Scenario Development
Time Series Analysis – Moving Averages
Econometric Models
Expert Opinion – Delphi Method
Monte Carlo Simulation
Research Analysis
Our research framework is built upon the fundamental principle of validating market intelligence from both demand and supply perspectives. This dual-sided approach ensures comprehensive market understanding and reduces the risk of single-source bias.
Demand-Side Analysis: We understand end-user/application behavior, preferences, and market needs along with the penetration of the product for specific application.
Supply-Side Analysis: We estimate overall market revenue, analyze the segmental share along with industry capacity, competitive landscape, and market structure.
Validation & Evaluation
Data triangulation is a validation technique that uses multiple methods, sources, or perspectives to examine the same research question, thereby increasing the credibility and reliability of research findings. In market research, triangulation serves as a quality assurance mechanism that helps identify and minimize bias, validate assumptions, and ensure accuracy in market estimates.
Custom Market Research Services
We will customise the research for you, in case the report listed above does not meet your requirements.
Get 10% Free Customisation